A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
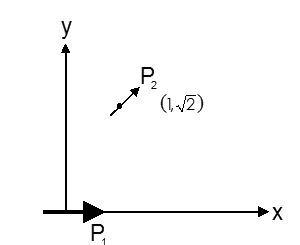
- Consider two electric dipoles P(1) and P(2) placed at (0, 0) and (1,...
Text Solution
|
- If each pair ofthe following three equations x: x^(2)+p(1)x+q(1)=0.x^(...
Text Solution
|
- If (1+x)^(n)=p(0)+p(1)x+p(2)x^(2)+....+p(n)x^(n) then (p(0)-p(2)+p(4)-...
Text Solution
|
- The polaroids P(1) and P(2) are placed in crossed position. A third po...
Text Solution
|
- Two Polaroids P(1) and P(2) are placed with their axis perpendicular t...
Text Solution
|
- Two point electric dipoles with dipole moment P(1) and P(2) are separa...
Text Solution
|
- The electric dipoles of moments p(1) and p(2) are in a straight line. ...
Text Solution
|
- यदि P(1) तथा P(2) दो विषम संख्याएँ है, जबकि p(1) gt p(2) तो p(1)^(2...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two electric dipoles P(1) and P(2) placed at (0, 0) and (1, s...
Text Solution
|