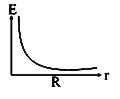
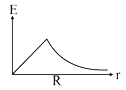
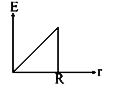
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In a uniformly charges sphere of total charge Q and radius R, the elec...
Text Solution
|
- In a uniformly charged sphere of total charge Q and radius R, the elec...
Text Solution
|
- A hallow metal sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The electric f...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field due to uniformly charged sphere of radius R as a fu...
Text Solution
|
- In a uniformly charges sphere of total charge Q and radius R, the elec...
Text Solution
|
- त्रिज्या R और सम्पूर्ण आवेश Q वाले एकसमान आवेशित गोले से विद्युत - क्ष...
Text Solution
|
- त्रिज्या R के एकसमान आवेशित (कुल आवेश =q ) कुचालक गोले के कारन विधुत क...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius R, is charged uniformly with total charge Q. Then c...
Text Solution
|
- Which graph best represents the variation of electric potential as a f...
Text Solution
|