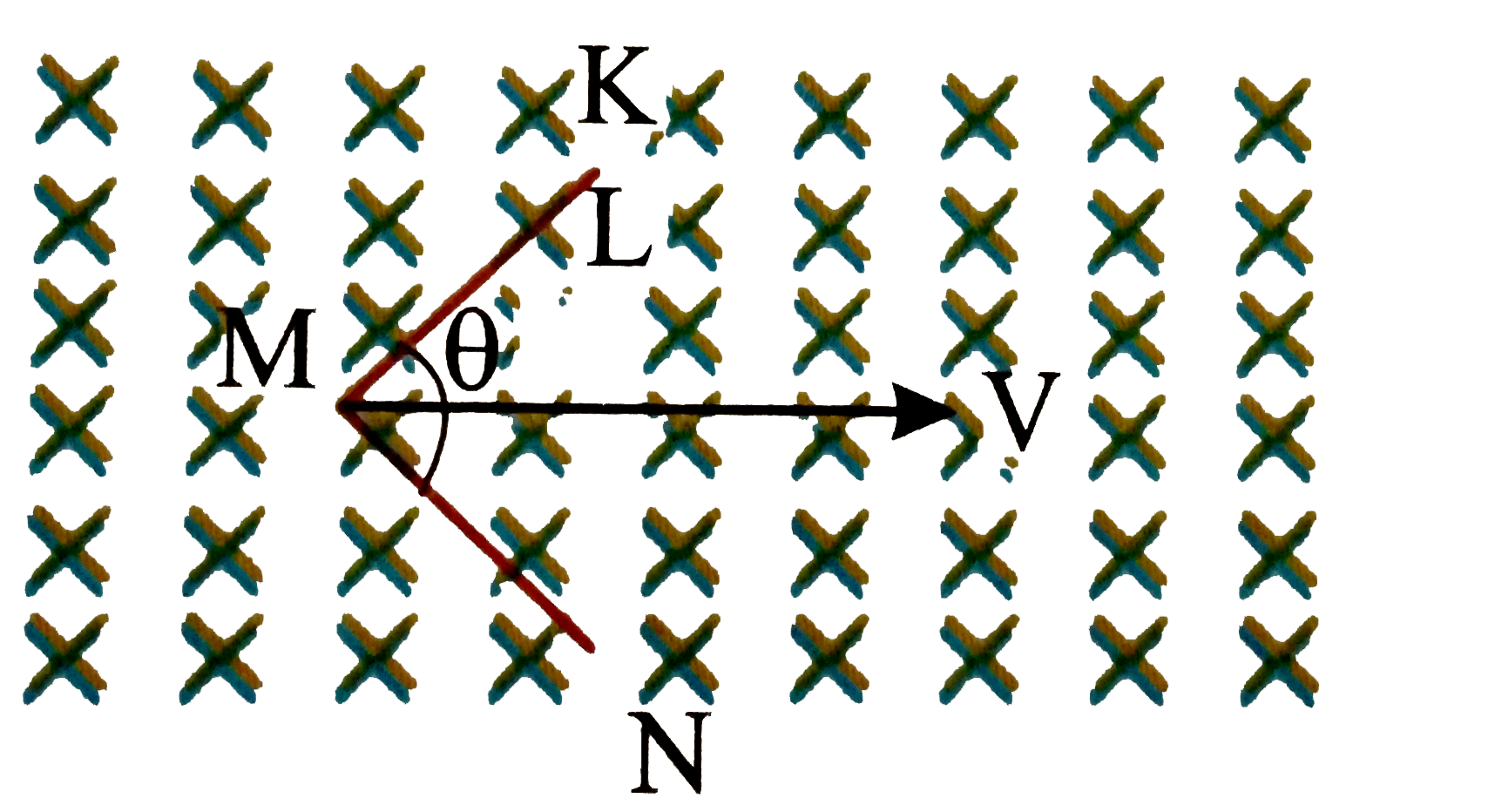Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A wire KMN moves along the bisector of the angle theta with a constant...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge -q and mass m enters a uniform magnetic field vec...
Text Solution
|
- A long conducting wire AH is moved over a conducting triangular wire C...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in Fig. A conducting wire HE is moved with a cons...
Text Solution
|
- A wire KMN moves along the bisector of the angle theta with a constant...
Text Solution
|
- A V-shaped conducting wire is moved inside a magnetic field as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में 2l लंबाई का एक सुचालक तार मध्यबिंदु O पर 2 theta कोण बनाते ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire is bent in the form of an angle theta . The wire mov...
Text Solution
|
- A V-shaped conducting wire is moved with a speed of v in a magnetic fi...
Text Solution
|