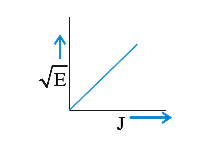
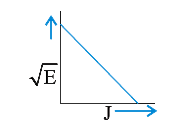
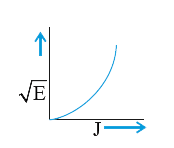
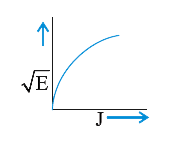
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The relation between angular momentum J of a body and rotational kinet...
Text Solution
|
- If J and E represent the angualr momentum and rotational kinetic energ...
Text Solution
|
- The angular momentum of electron in a given orbit is J . Its kinetic e...
Text Solution
|
- घूर्णन गतिज ऊर्जा E तथा कोणीय संवेग J में क्या सम्बन्ध होता है ?
Text Solution
|
- A body of moment of inertia 2kg-m^(2) has a rotational kinetic energy ...
Text Solution
|
- The relation between Rotation Kinetic Energy and angular momentum is
Text Solution
|
- The graph between the angular momentum J and angular velocity omega wi...
Text Solution
|
- The relation between angular momentum J of a body and rotational kinet...
Text Solution
|
- The kinetic energy of rotation K depends on the angular momentum J and...
Text Solution
|