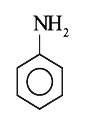
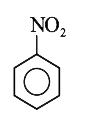
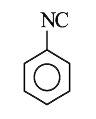
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A overset( "reduction ") to B overset(CHCl3 //KOH ) to C overset("...
Text Solution
|
- If overset(to)(a),overset(to)(b),overset(to)(c ) are three non-zero ,...
Text Solution
|
- A underset(अपचयन )overset("reduction")(to) B overset(CHCI(3)//KOH)(to)...
Text Solution
|
- 2, 2-dichlorpropane overset("Aq,KOH")to A underset("reduction")overset...
Text Solution
|
- C8H8Cl2(A)overset("Aq. NaoH")rarr(B)overset("Mild reduction")rarr(C)ov...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound ( A ) on reduction gives compound (B) on tr...
Text Solution
|
- C2H5Broverset(AgCN)toAoverset(H3overseto+O)toB+HCOOH Bunderset"KOH"ove...
Text Solution
|
- C2H5Br overset(AgCN)(to)overset(H(3)overset(o+)(O))(to)B+HCOOHBunderse...
Text Solution
|
- CH3NO2overset(Sn2"/"HCl)(to)A underset(" alcoholic KOH ") overset(CHCl...
Text Solution
|