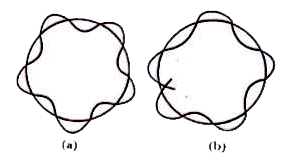
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS|22 VideosATOMIC STRUCTURE
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|18 VideosAP MARCH-2018 I.P.E. PAPER
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SECTION-C|5 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-ATOMIC STRUCTURE-LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Explain Rutherford 's nuclear of an atom . What are its drawbacks ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the influence of Planck's quantum theory on Bohr's model of st...
Text Solution
|
- What are the postulates of Bohr's model of hydrogen atom ? Discuss the...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the success of Bohr's theory for hydrogen atom.
Text Solution
|
- What are the consequences that lead to the development of quantum mech...
Text Solution
|
- What are the main features of quantum mechanical model of an atom?
Text Solution
|
- What are the limitation of Bohr's model of an atom?
Text Solution
|
- What are the evidence in favour of dual behaviour of electron?
Text Solution
|
- How are the quantam numbers n, l and m arrived at ? Explain the signif...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the dual behaviour of matter. Discuss its significance to micr...
Text Solution
|
- What are various ranges of electromagnetic radiation ? Explain the cha...
Text Solution
|
- Define atomic orbital . Explain the shapes of s, p and d orbitals with...
Text Solution
|
- Explain diagrammatically the boundary surfaces for three 2p orbitals a...
Text Solution
|
- IIIustrate the reaasons for the stability of completey filled and half...
Text Solution
|
- Explain emission and absorption spectra. Discuss the general descripti...
Text Solution
|