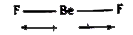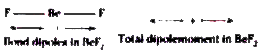Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|9 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|9 VideosATOMIC STRUCTURE
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS|22 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM AND ACIDS-BASES
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE-SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Explain why H(2)O has dipolemoment while CO(2) does not have.
Text Solution
|
- Define Dipolemoment. Write its applications.
Text Solution
|
- Explain why BeF(2), molecule has zero dipolemoment although the Be-F b...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the structure of CH(4) molecule.
Text Solution
|
- Explain Polar Covalent bond with a suitable example.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the shape and bond angle in BCl(3) molecule in terms of Valenc...
Text Solution
|
- What are sigma " and " pi bonds ? Specify the differences betweeen the...
Text Solution
|
- Even though nitrogen in ammonia is in sp^(3) hybridization, the bond a...
Text Solution
|
- Show how a double and triple bond are formed between carbon atoms in ...
Text Solution
|
- Show how a double and triple bond are formed between carbon atoms in ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain hybridisation of phosphorous in the formation of PCl(5)
Text Solution
|
- Explain the hybridisation involved is SF(6).
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation of Coordinate Covalent bond with one example.
Text Solution
|
- Which hybrid orbitals are used by Carbon atoms in the following molecu...
Text Solution
|
- Which hybrid orbitals are used by Carbon atoms in the following molecu...
Text Solution
|
- Which hybrid orbitals are used by Carbon atoms in the following molecu...
Text Solution
|
- Which hybrid orbitals are used by Carbon atoms in the following molecu...
Text Solution
|
- Explain different types of hydrogen bonds with examples.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation H(2) molecule on the basis of Valence Bond theor...
Text Solution
|
- Using Molecular Orbital Theory explain why the B(2) molecule is parama...
Text Solution
|