The valence bond theory explains the shape, the formation and directional properties of bonds in poly atomic molecules like `BeCl_(2), BCl_(3), CH_(4), NH_(3), H_(2)O`, etc. in terms of overlap and hybridisation of atomic orbitals.
E.g., in `BeCl_(2)`, Be is the central atom. Its atomic number is 4. Therefore its ground state electron configuration is `1s^(2)2s^(2)`. In order to explain the formation of `BeCl_(2)`, SP hybridisation is to be assumed for Be in its excited state. The excited state configuration of Be is `1s^(2)2s^(1)2p_(x)^(1)2p_(y)^(0)2p_(z)^(0)`. As a result of which two sp hybrid orbitals will form on it. Now the two sp hybrid orbirtals overlap Head-Head with `3p_(z)` orbitals of two chlorine atoms forming two sigma bonds.
The molecule is linear and the bond angle is `180^(@)`.

In `BCl_(3)` the central atom is boron. Its atomic number is 5. Therefore its ground state electron configuration is `1s^(2)2s^(2)2p_(x)^(1)2p_(y)^(0)2p_(z)^(0)`. Form this configuration it is evident that it exhibits mono-valency. The first excited state configuration of B is `1s^(2)2s^(1)2p_(x)^(1)2p_(y)^(0)2p_(z)^(0)`. Since, there are two half-filled orbitals, the valency of Boron is 3.
In order to explain the formation of `BCl_(3)` molecule `sp^(2)` hybridisation is to be assumed to boron atom in its excited state I. As a result of which three `sp^(2)` hybrid orbitals will form on it. Now, the three `sp^(2)` hybrid orbitals of 'B' atom overlap Head - Head with `3p_(z)` orbitals of three Cl atoms forming three sigma bonds. 'The shape of the molecule is plane triangular is plane triangluar and the bond angle is `120^(@)`.

`CH_(4)` (Methane) : In `CH_(4)` the central atom is carbon. Its atomic number is 6. Therefore the electron configuration is `1s^(2)2s^(2)2p^(2)(2p_(x)^(1),2p_(y)^(1),2p_(z)^(@))`. In order to explain the formation of four bonds excited state configuration `(1s^(2)2s^(1)2p_(x)^(1)2p_(y)^(1)2p_(z)^(1))` is to be taken. From this configuration, we can say that carbon can form four bonds. `[Ex. CH_(4)]`
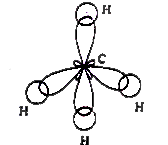
In the formation of methane molecule the central carbon atom undergoes `sp^(3)` hybridisation in its excited state `(1s^(2)2s^(1)2p_(x)^(1)2p_(y)^(1)2p_(z)^(1))`. As a result of which four `sp^(3)` hybrid orbitals form on it. Each of them contains an unpaired electron. Now, these four hybrid orbitals overlap Head-Head with 1s orbitals of four hydrogen atoms forming `CH_(4)` molecule. The strucrture of the molecule is tetrahedral. The bond angle is `109^(@)28'`. Since there are no lone pairs, there is no distortion in the structure of the molecule.
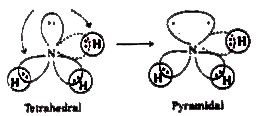
`NH_(3)` (Ammonia) in `NH_(3)` molecule, one `sp^(3)` orbital contains a lone pair of electrons. There will be repulsions between the lone pair and bond pair electrons. These are stronger than bp - bp repulsions. `(l.p-b.p gt b.p-b.p)`. So the bond pairs are pushed together. Hence the bond angle decreases from tetrahedral angle. The molecule assumes a pyramidal shape.