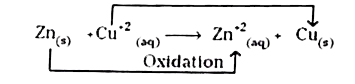Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
STOICHIOMETRY
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTION|13 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS|10 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS|10 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTION & ANSWERS|10 VideosTHE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS - GROUP 13
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-STOICHIOMETRY-SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Calculate the volume of oxygen gas required at STP conditions for the ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the volume of H(2) liberated at 27^(@)C and 760 mm of Hg pre...
Text Solution
|
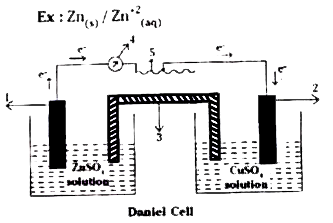
- Explain the role of redox reactions in titrimetre processes and galvan...
Text Solution
|
- Define and explain molar mass.
Text Solution
|
- What are disproportionate reactions? Give example.
Text Solution
|
- What is comproportionation reactions? Give example.
Text Solution
|
- Determine the empirical formula of an oxide of iron which has 69.9% ir...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the mass of sodium acetate (CH(3)COONa) required to make 500...
Text Solution
|
- What is the concentration of sugar (C(12)H(22)O(11)) in mol L^(-1) if ...
Text Solution
|
- How many significant figures are present in the following ? i) 0.002...
Text Solution
|
- Round up the following upto three significant figures : i) 34.216, i...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the molarity of a solution of ethanol in water in which the ...
Text Solution
|
- A welding fuel gas contains carbon and hydrogen only. Burning a small ...
Text Solution
|
- Calcium Carbonate reacts with aqueous HCl to give CaCl(2)andCO(2) acco...
Text Solution
|
- Chlorine is prepared in the laboratory by treating manganese dioxide (...
Text Solution
|
- To 50 ml. of 0.1 N Na(2)CO(3) solution 150 ml. of H(2)O is added. Then...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the volume of 0.1 N H(2)SO(4) required to neutralise 200 ml....
Text Solution
|
- Calculate normality of H(2)SO(4) solutions if 50 ml of it completely n...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the volume of 0.1MKMnO(4) required to react with 100 ml. of ...
Text Solution
|
- Assign oxidation number to the underlined elements in each of the foll...
Text Solution
|