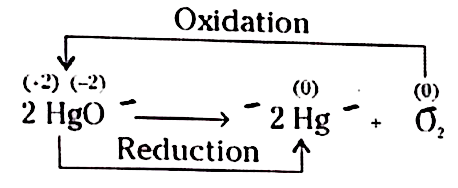
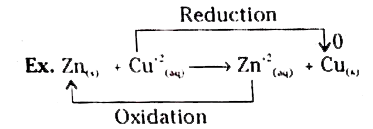Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
STOICHIOMETRY
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS & ANSWERS|10 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|56 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTION & ANSWERS|10 VideosTHE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS - GROUP 13
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-STOICHIOMETRY-LONG ANSWER QUESTION
- Write the balanced ionic equation which represents the oxidation of io...
Text Solution
|
- Write the balanced ionic equation for the oxidation of sulphite ions t...
Text Solution
|
- Oxalic acid is oxidised by permanganate ion in acid medium of Mn^(2+) ...
Text Solution
|
- Phosphorus when heated with NaOH solution gives Phosphine (PH(3))andH(...
Text Solution
|
- Balance the following equation. Cr(OH)(3)+IO(3)^(-)overset(OH^(-))(t...
Text Solution
|
- Balance the following equation by the oxidation number method. MnO(4...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the different types of redox reactions.
Text Solution
|
- State the law of definite proportions. Suggest one problem to understa...
Text Solution
|
- How are the end points of titrations detected in the following reactio...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the amount of Carbondioxide that could be produced when i)...
Text Solution
|
- Dinitrogen and dihydrogen react with each other to produce ammonia acc...
Text Solution
|
- Assign oxidation number to the underlined elements in each of the foll...
Text Solution
|
- What are the oxidation numbers of the underlined elements in each of t...
Text Solution
|