Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise Short Answer Questions|17 VideosMOST IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|11 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTION & ANSWERS|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Long Answer Questions
- Explain the following : a) Column chromatography
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following : b) Thin layer chromatography
Text Solution
|
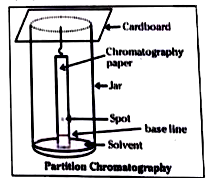
- Explain the following : c) Partition chromatography
Text Solution
|
- Explain the estimation of nitrogen of an organic compound by a) Duma...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the estimation of nitrogen of an organic compound by b) Kjel...
Text Solution
|
- Explain inductive effect with a suitable example.
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on mesomeric effect.
Text Solution
|
- Describe resonance effect with one example.
Text Solution
|
- Explain how many types of organic reactlons are possible.
Text Solution
|
- Write the possible conformations of ethane and explain which is more s...
Text Solution
|
- Explain aromatic electroplhilic substitution reactions of benzene.
Text Solution
|
- Explain electrophilic addition reactions of ethylene with mechanism.
Text Solution
|
- With the help of mechamism explain free radical halogenationis of allk...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss Markovnikov's rule and Kharash effect.
Text Solution
|
- How would you convert the following compounds into benzene ? Chloro...
Text Solution
|
- How would you convert the following compounds into benzene ? Toluene
Text Solution
|
- How would you convert the following compounds into benzene ? p - nit...
Text Solution
|
- Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes con...
Text Solution
|
- Write the equations involved in the detection of Nitrogen, Halogens an...
Text Solution
|
- How are carbon and hydrogen of an organic compound estimated?
Text Solution
|