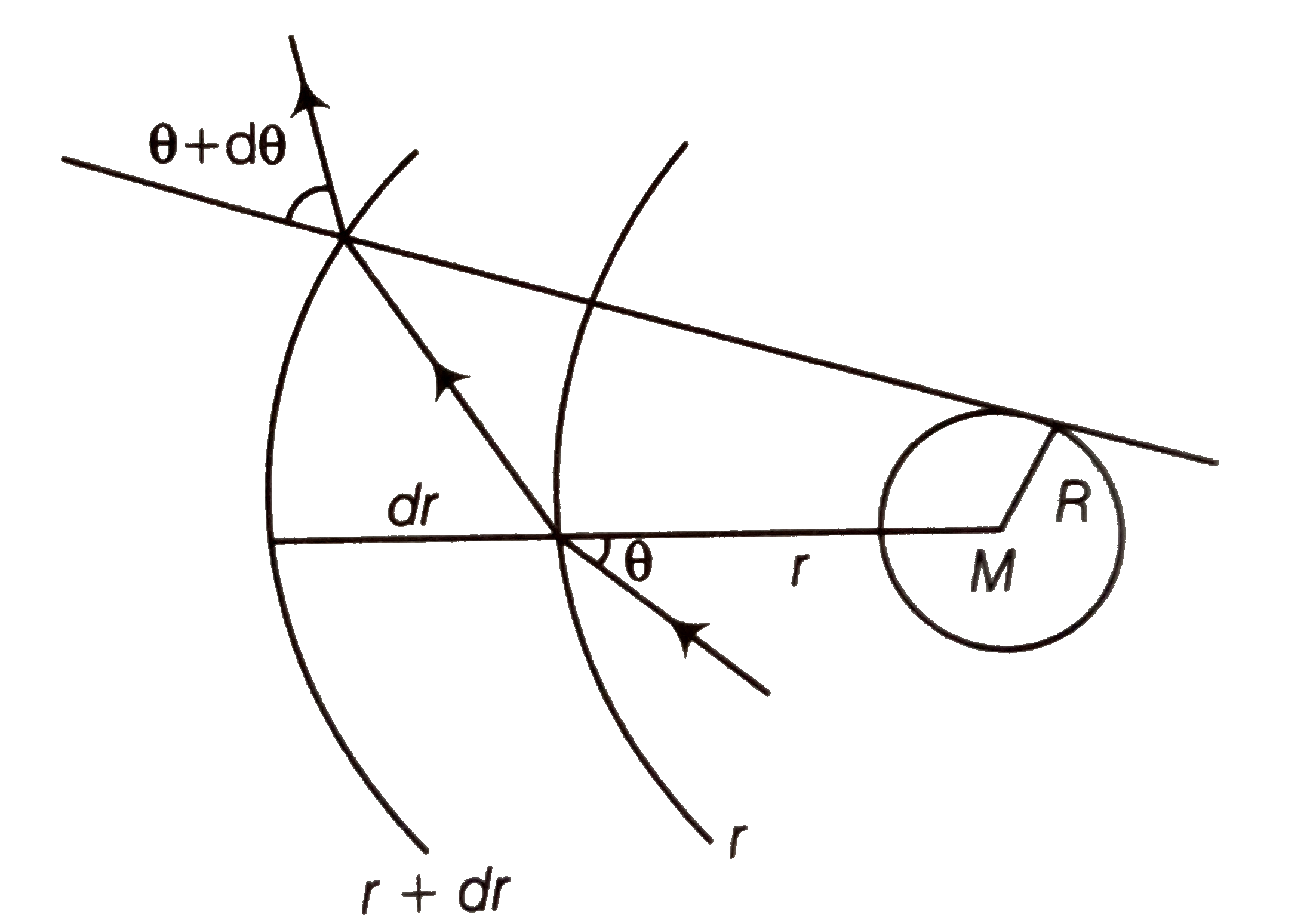
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS -Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
- A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is...
Text Solution
|
- Between the primary and secondary rainbows, there is a dark band known...
Text Solution
|
- A magnifying glass is used, as the object to be viewed can be brought ...
Text Solution
|
- An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length ...
Text Solution
|
- Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less th...
Text Solution
|
- The near vision of an average person is 25 cm. To view an object with ...
Text Solution
|
- An unsymmeterical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point o...
Text Solution
|
- Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 gt d2 gt d3 and refractive in...
Text Solution
|
- The angle of minimum deviation for a glass prism with mu=sqrt3 equals ...
Text Solution
|
- A short object of length L is placed along the principal axis of a con...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of radius 'R' is placed co-axially and horizontally in...
Text Solution
|
- A thin convex lens of focal length 25 cm is cut into two pieces 0.5 cm...
Text Solution
|
- In many experimental set-ups the source and screen are fixed at a dist...
Text Solution
|
- A jar of height h is filled wih a transparent liquid of refractive ind...
Text Solution
|
- A myopic adult has a far point at 0.1 m. His power of accomodation is ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that for a material with refractive index mu ge sqrt(2), light in...
Text Solution
|
- The mixture of a pure liquid and a solution in a along vertical column...
Text Solution
|
- If light passes near a massive object, the gravitational interaction c...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely long cylinder of radius R is made of an unusual exotic m...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (...
Text Solution
|