Nucleic acids are long chain macromolecules which are formed by end to end Ans. polymerisation of large number of repeated units called nucleotides. Nucleic acids show a wide range of secondary structures. A secondary structure is the set of InteractIons between bases and sugar phosphate backbone and is responsible for the shape that nucleic acid.
James Watson and Francis Crick proposed a secondary structure of DNA molecules based on the crystallographic studies.
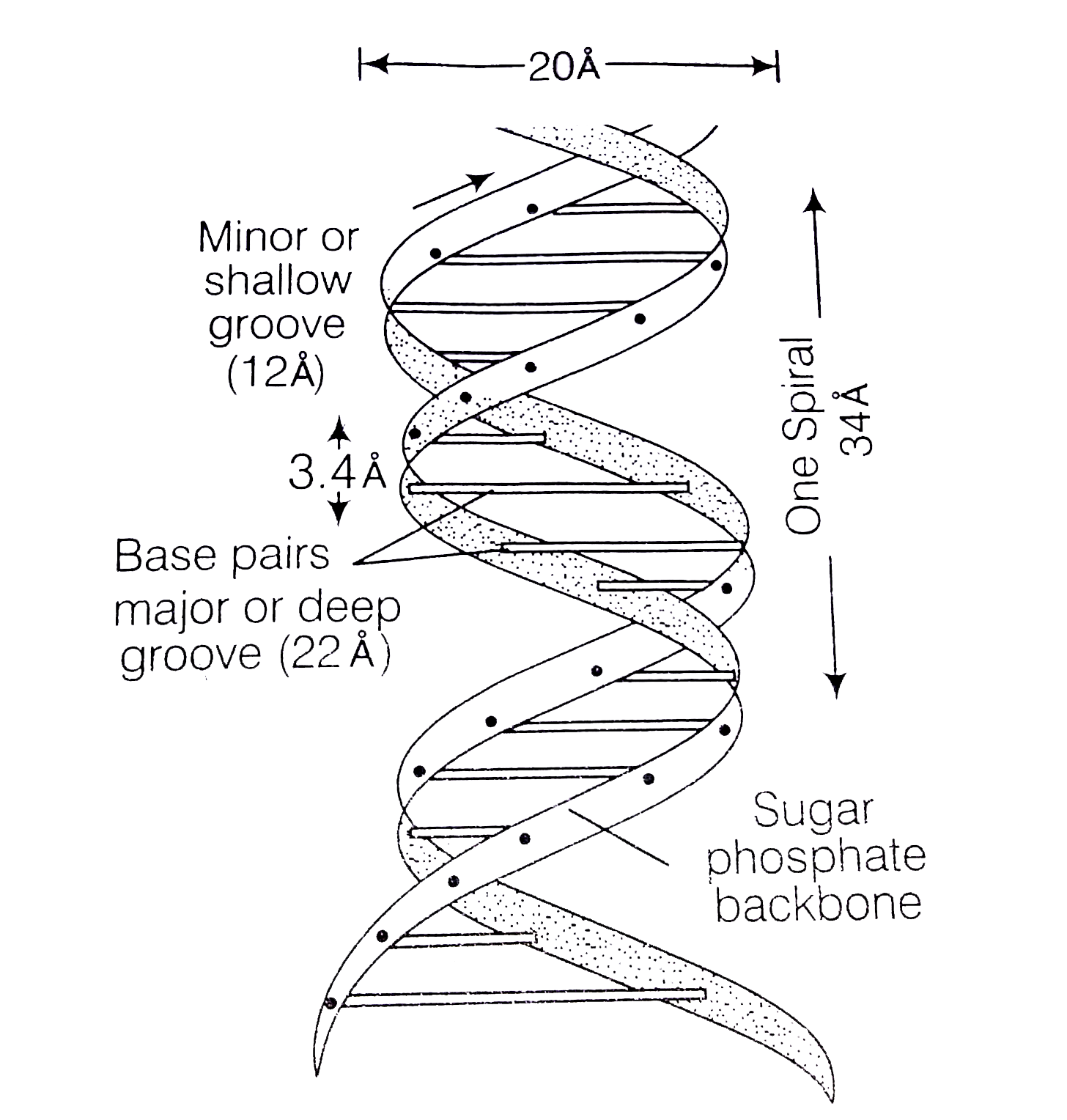
(i) DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a helically twisted double-chain polydeoxyribo- nucleotide macromolecule.
(ii) The two strands of DNA run anti-parallely to each other called as DNA duplex.
(iii) The spiral twisting of DNA has two types of alternate grooves, i.e., major and minor.
(iv) One turn of `360^(@)` of the spiral has about 10 nucleotides on each strand of DNA, occupying a distance of about 3.4 nm.
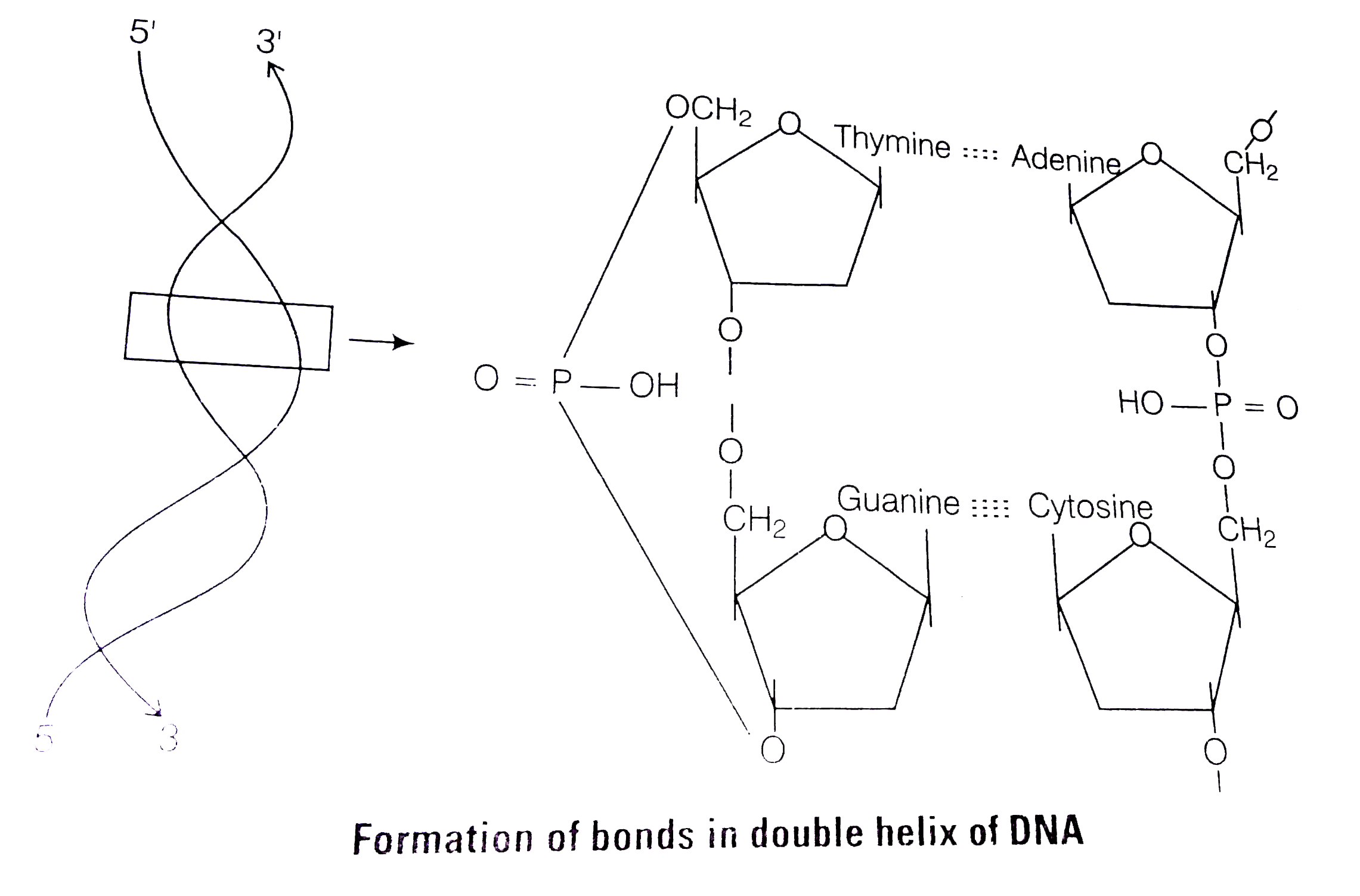
(v) The nucleotides within each strand are held together by the phosphodiester bonds between the 5' carbon of one nucleotide and the 3' carbon of the adjacent nucleotide. These strong covalent bonds holds the sugar/phosphate backbone together.
(vi) The two strands of DNA are held together by weak hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. These hydrogen bonds are base specific. That is adenine forms 2 hydrogen bonds with thymine CA= T and cytosine forms 3 hydrogen bonds with guanine `(CequivG)`
(vii) As specific and different nitrogen bases occur on two DNA chains, they are said to be complementary, i.e., purine lies opposite to pyrimidine. This purine-pyrimidine pairing also contributes to the thickness of strand, i.e., 2nm, and makes the two chains complementary