Formation of cross-bridge between the actin and myosin filament help muscle to contract.
(i) An ATP molecule joins the active site on myosin head of myofilament. These heads contains an enzyme, myosin ATPase that along with `Ca^(2+) and Mg^(2+)` ions catalyses the breakdown of ATP.
`ATPunderset(Ca^(2+)Mg^(2+))overset("Myosin ATPase")rightarrowADP+P_(i)+"Energy"`
(ii) The energy is transferred to myosin head which energises and straightens to join an active site on actin myofilament, forming a cross-bridge.
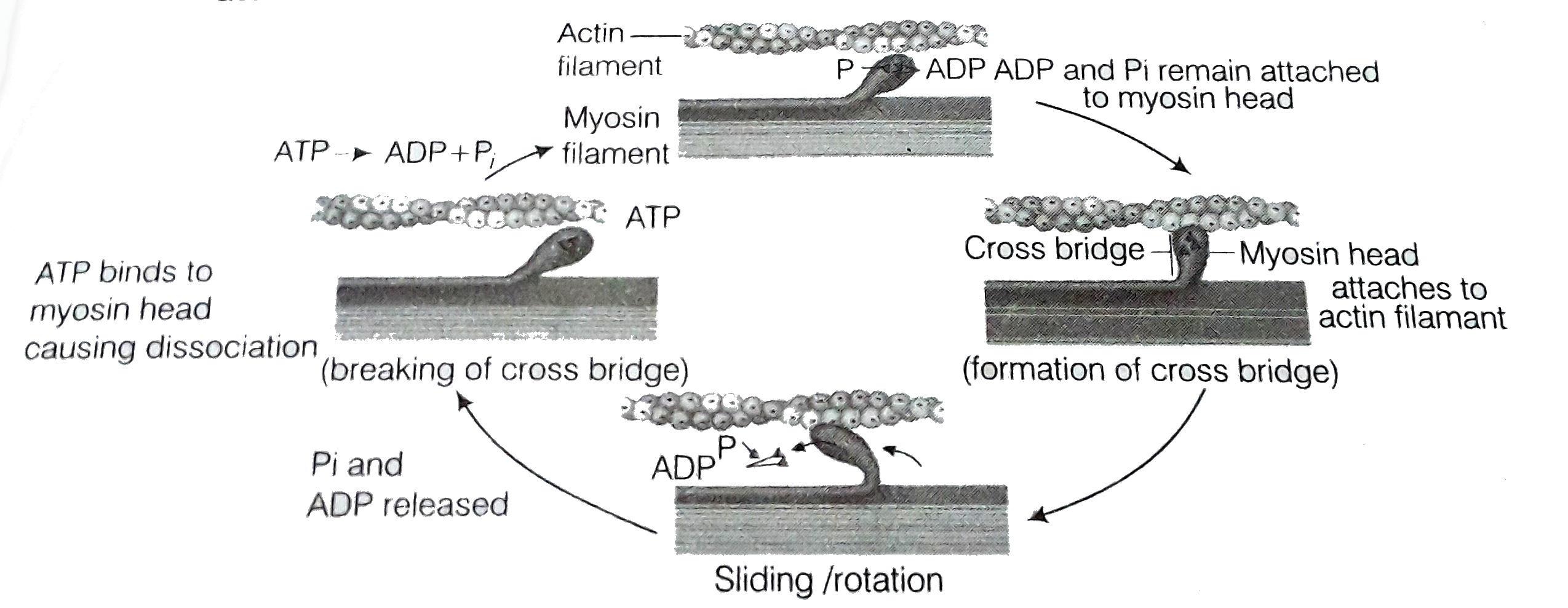
(iii) The energised cross-bridges move, causing the attached actin filaments to move towards the centre of A-band. The Z-line is also pulled inwards causing shortening of sarcomere, i.e., contraction. It is clear from the above explanation that during contraction A-bands retain the length, while I-bands get reduced.
(iv) The myosin head releases ADP and Pi, rekaxes to its low energy state. The head detaches from actin myofilaments when new ATP molecule joins it and cross-bridge are broken.
(v) In repeating cycle, the free head cleaves the new ATP. The cycles of cross-bridge formation and breakage is repeated causing further sliding.
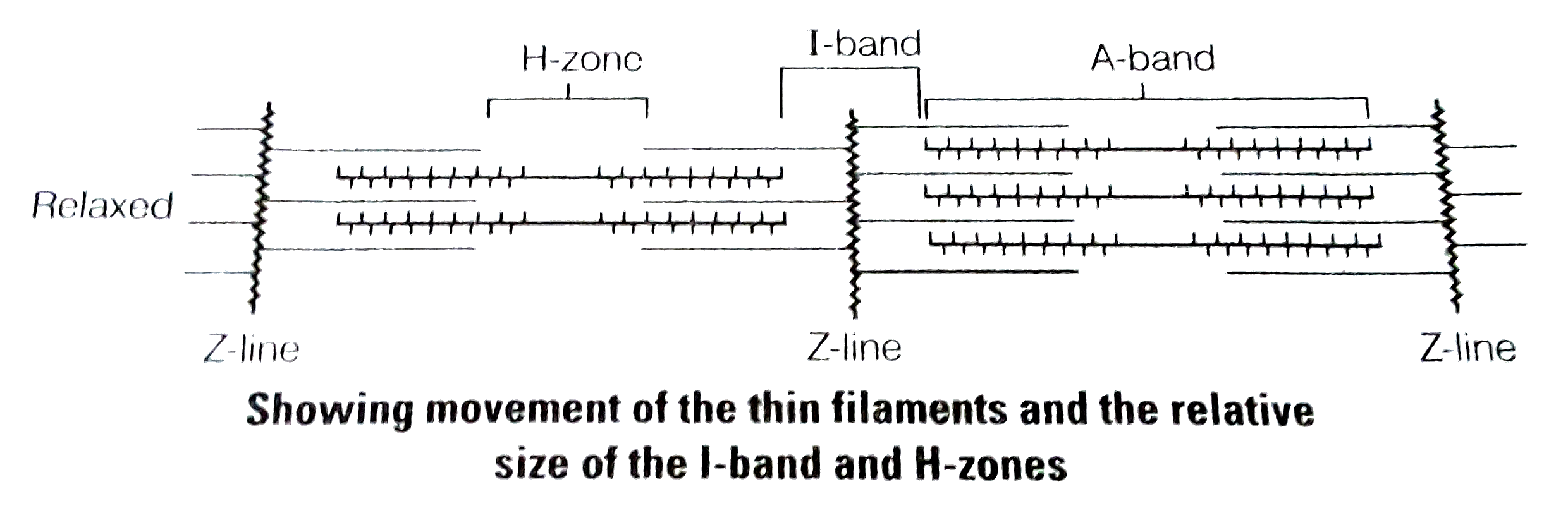
(vi) Muscle relaxation occurs after contraction when the calcium ions are pumped back to the sarcoplasmic cisternae, thus, blocking the active sites on actin myofilaments. The Z-line returns to original position, i.e., relaxation.

