A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise VSATQ|10 VideosBREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise SATQ|7 VideosBody Fluids and Circulation
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE Q|5 VideosCELL : THE UNIT OF LIFE
NCERT EXEMPLAR|Exercise Long Answer Type Questions|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASES-SATQ
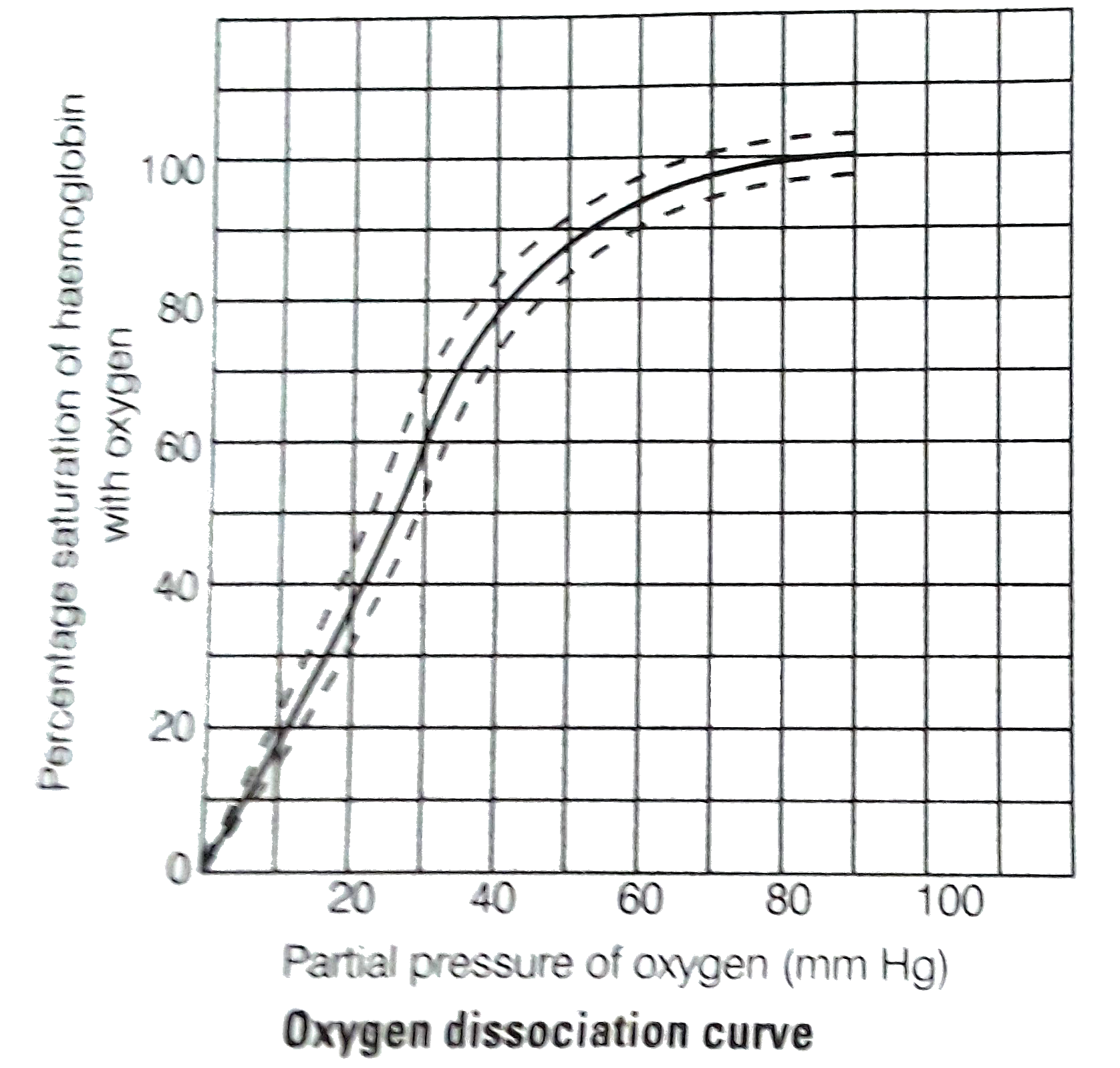
- The oxygen - haemoglobin dissociation curve will show a right shift in...
Text Solution
|
- State the different modes of CO(2) transport in blood.
Text Solution
|
- Compared to O(2) diffusion rate of CO(2) through the diffusion membran...
Text Solution
|
- Given below is a list of different steps (i-vi) involved in respiratio...
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between (a) Insiratory and expiratory reserve volume ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the transport of O(2) " and " CO(2) between alveoli and tissue...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the mechanism of breathing with neat labelled sketches.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the role of neural system in regulation of respiration.
Text Solution
|