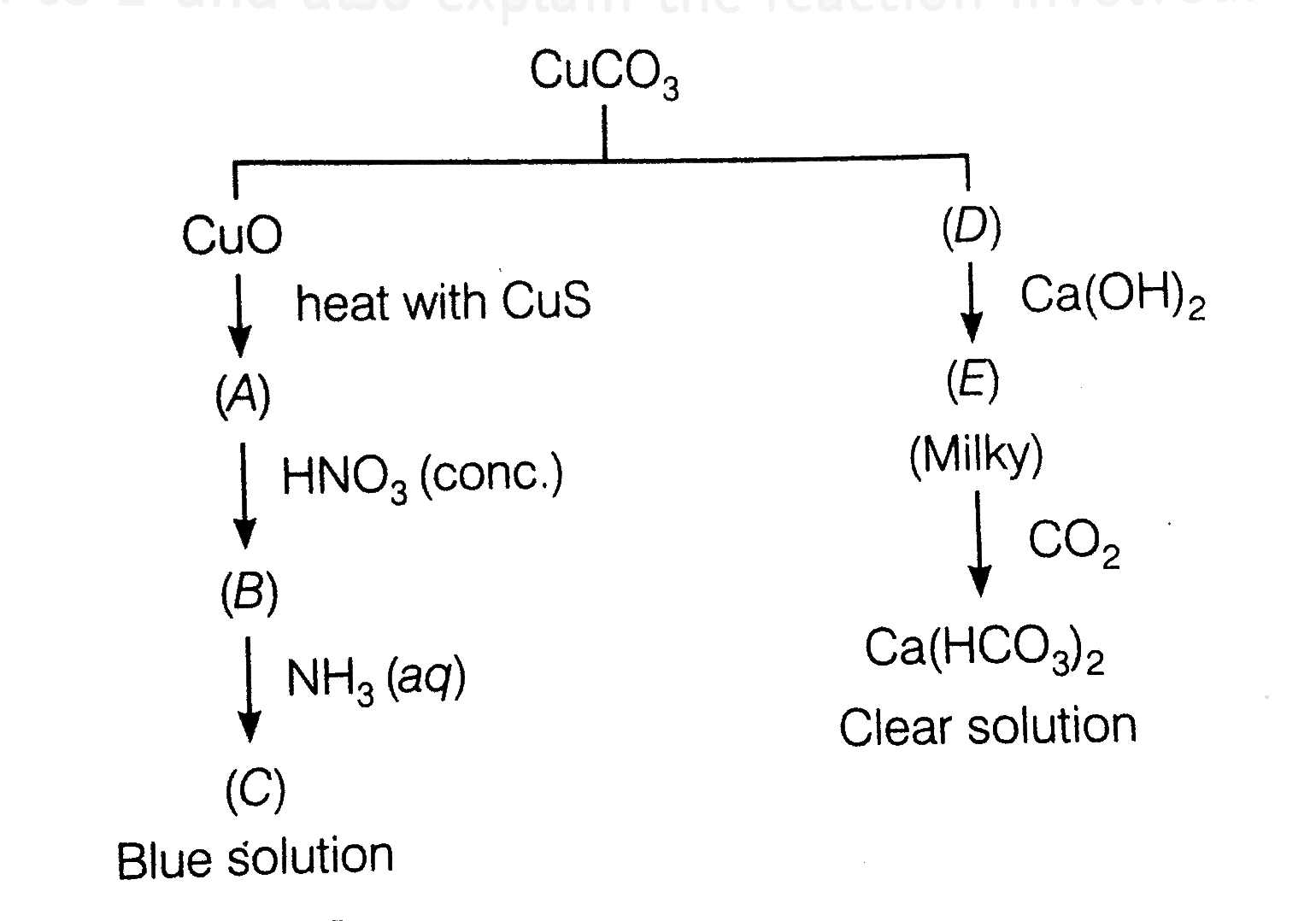Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-D AND F-BLOCK ELEMENTS-D And F-Block Elements
- Match the catalyst given in Column I with the processes given in Colum...
Text Solution
|
- Match the compounds/elements given in Column I with uses given in Colu...
Text Solution
|
- Match the properties given in Column I with the metals given in Column...
Text Solution
|
- Match the statements given in Column I with the oxidation states given...
Text Solution
|
- Match the solutions given in Column I and the colours given in Column ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the property given in Column I with the element given in Column ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the properties given in Column I with the metals given in Column...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Cu^(2+) iodine is not known. Reason (R ) Cu^(2+) oxidi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Separation of Zr and Hf is difficult. Reason (R ) Bec...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Actinoids form relatively less stable complexes as compa...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Cu cannot liberate hydrogen from acids. Reason (R ) B...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) The highest oxidation state of osmium is +8. Reason (...
Text Solution
|
- Identify A to E and also explain the reaction involved.
Text Solution
|
- When a chromite ore (A) is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess ...
Text Solution
|
- When an oxide of manganese (A) is fused with KOH in the presence of an...
Text Solution
|
- On the basis of lanthanoid contraction, explain the following: (i)...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions (i) Which element of the first transi...
Text Solution
|
- Mention the type of compounds formed when small atoms like H, C and N ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change t...
Text Solution
|
- A violet compound of manganese (A) decomposes on heating to liberate o...
Text Solution
|