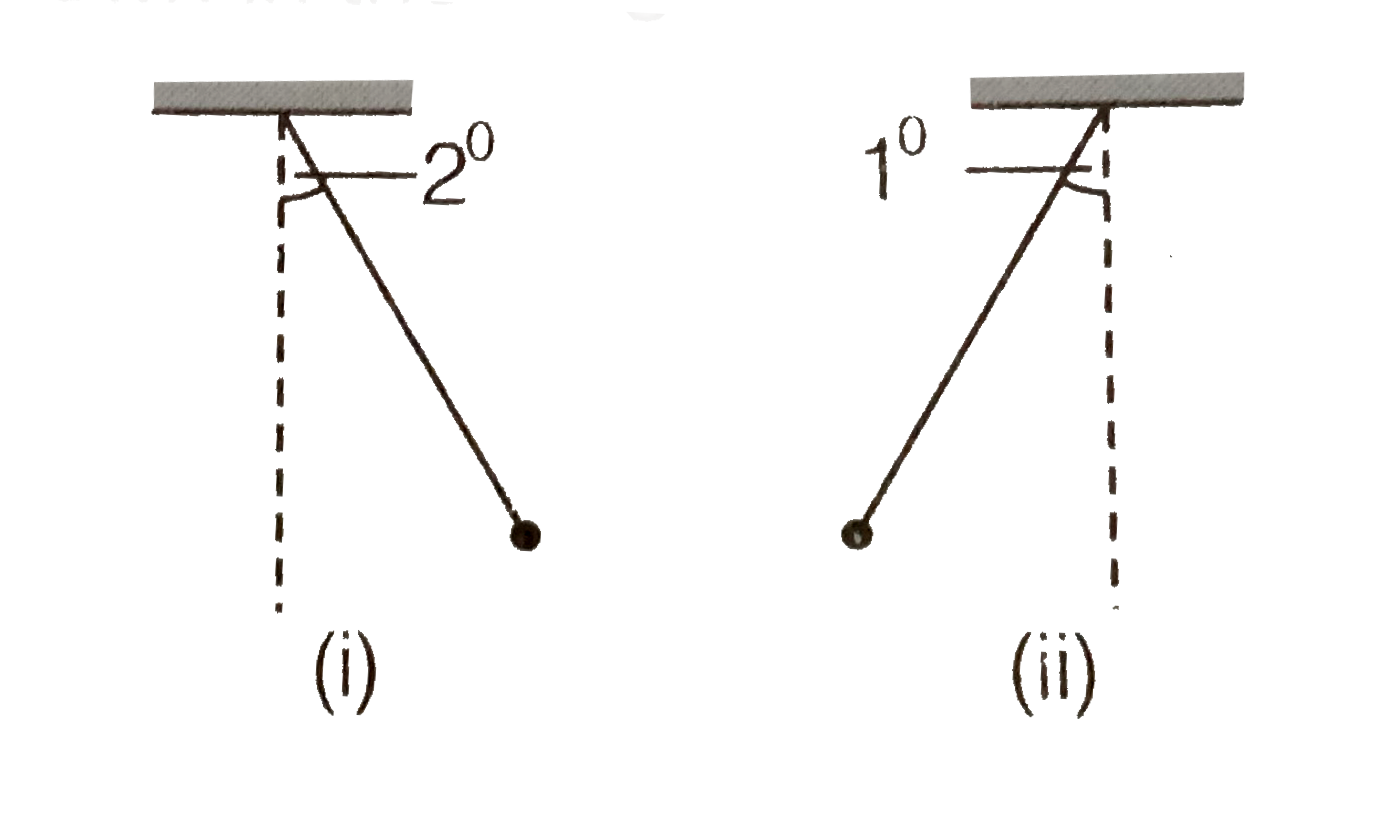
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-OSCILLATIONS-MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs)
- What are the two basic characteristics of a simple harmonic motion?
Text Solution
|
- When will the motion of a simple pendulum be simple harmonic?
Text Solution
|
- What is the ration of maximum acceleration to the maximum velocity of ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the ration between the distance travelled by the oscillator in...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, what be the sign of the velocity of the point P', which is ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that for a particle executing SHM, velocity and dispacement have ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a graph to show the variation of PE, KE and total energy of a sim...
Text Solution
|
- The length of a second's pendulum on the surface of earth is 1 m. What...
Text Solution
|
- Find the time period of mass M when displaced from its equilibrium pos...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the motion of a particle represented by y=sinomegat-cosomega...
Text Solution
|
- Find the displacement of a simple harmonic oscillator at which its PE ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is situated in potential field U(x)=U(o)(1-cospropx) ...
Text Solution
|
- A mass of 2kg is attached to the spring of spring constant 50Nm^(-1). ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a pair of identical pendulums, which oscillate with equal amp...
Text Solution
|
- A person normally weighing 50 kg stands on a massless platform which o...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is attached ot one end of a massless spring which is ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical log of wood of height h and area of cross-section A floa...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a V-tube containing mercury is connected ot a suction pump ...
Text Solution
|
- A tunnel is dug through the centre of the earth. Shwo that a body of m...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of time period 1s and length l is hung from a fixed ...
Text Solution
|