Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-THERMODYNAMICS -LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Consider a P-V diagram in which the path followed by one mole of perfe...
Text Solution
|
- A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cy...
Text Solution
|
- A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of an ideal gas in...
Text Solution
|
- Consider that an idela gas (n mole) is espanding in a process gives b...
Text Solution
|
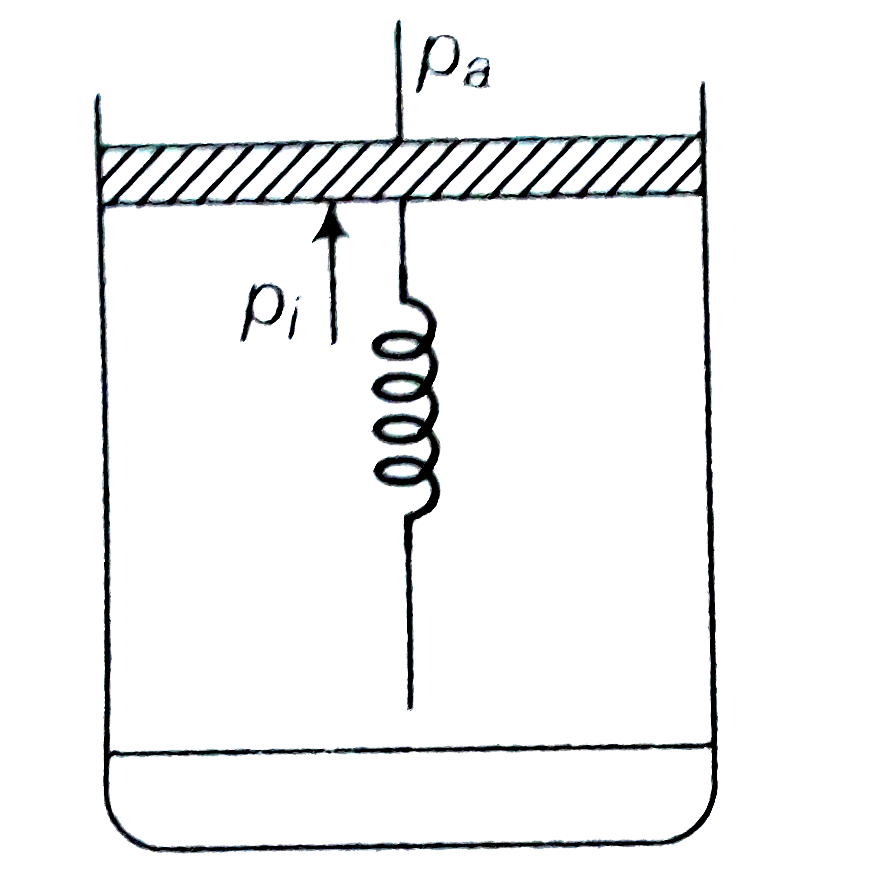
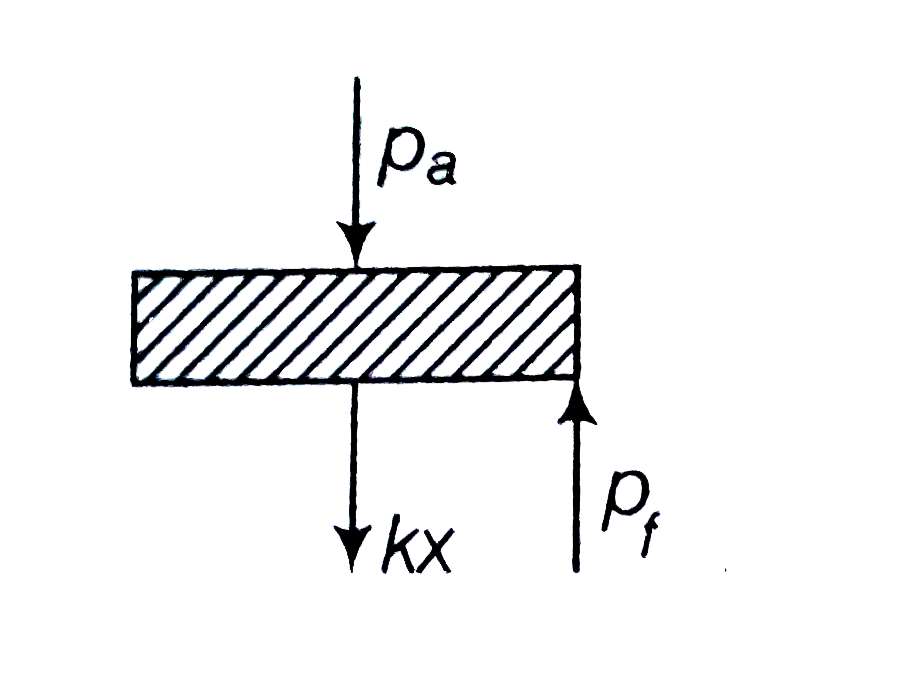
- Consider one mole of perfect gas on a cylinder of units cross-sect...
Text Solution
|