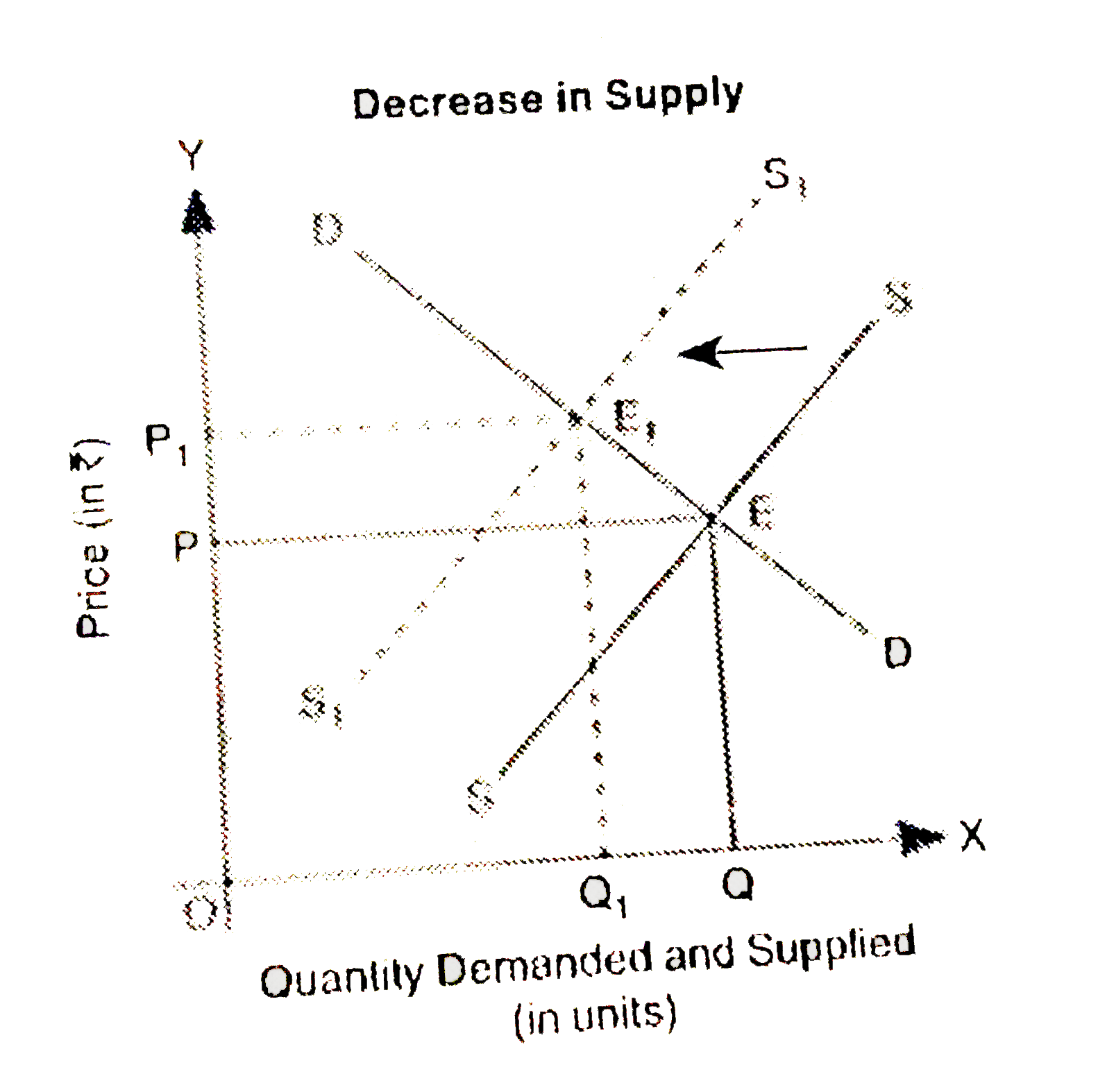
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SANDEEP GARG-DEMAND AND ITS DETERMINANTS-Model test paper 3
- Which of the following is a statement of normative nature in economics...
Text Solution
|
- Define Marginal Physical Product
Text Solution
|
- A firm is operating with a Total Variable cost of Rs 500 when 5 units ...
Text Solution
|
- In an imperfectly competitive market, if the Total Revenue is maximum,...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the characteristics of Production Possibility Frontier. OR ...
Text Solution
|
- Giving reason, state the impact of each of following on demand curve o...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Arrange the following coefficients of price elasticity of demand i...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the concept of 'buffer stock' as a tool of price floor OR ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how the following factors effect the supply of the commodity. ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A consumer, Mr Aman is in state of equilibrium consuming two good ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Why is Total Variable Cost curve inverse S-shaped? (b) What is A...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the value of demand and supply curves of a commodity-X is give...
Text Solution
|