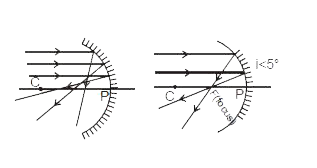Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
MOTION|Exercise Exercise - 1 Section A - Plane Mirror|12 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
MOTION|Exercise Exercise - 1 Section B, C, D, E - Mirror formula and Magnification, Velocity in Spherical Mirror, Cutting of Mirrors, Combination of Mirrors, Intensity of light|10 VideosFLUID
MOTION|Exercise Exercise-4 level-II|5 VideosGRAVITATION
MOTION|Exercise Exercise - 4 Section - B Previous Years Problems|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Exercise - 4 | Level-II
- Find the distance CQ if incident light ray parallel to principal axis ...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of powers of a thin convex and thin concave lens is 3/2 and ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows object O. Final image I is formed after two refractions a...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the minimum angle of incidence such that the total intern...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical prism of index sqrt3 are kept as shown in the figure. A ...
Text Solution
|
- A point object is placed at a distance of 20cm from a thin plano-conve...
Text Solution
|
- Graph of position of image vs position of point object from a convex l...
Text Solution
|
- Parallel rays of light from Sun falls on a biconvex lens of focal leng...
Text Solution
|
- A simple telescope used to view distant objects has eyepiece and objec...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in water is incident on its surface open to ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1 The formula connecting u,v and f for a spherical mirror is...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment to determine the focal length (f) of a concave mirror...
Text Solution
|
- Two beam of red and violet colors are made to pass separately through ...
Text Solution
|
- A light beam is traveling from Region I to region IV (refer figure). T...
Text Solution
|
- An optical component and an object S placed along its optic axis are g...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from a height of 20 m above the surface of water in ...
Text Solution
|
- A student performed the experiment of determination of focal length of...
Text Solution
|
- A ray OP of monochromatic light is incident on the face AB of prism AB...
Text Solution
|
- The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20 cm. When an object is m...
Text Solution
|
- A biconvex lens of focal length 15 cm is in front of a plane mirror. T...
Text Solution
|
- A large glass slabe (mu=5//3) of thickness 8cm is placed over a point ...
Text Solution
|