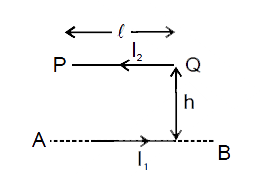Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-MAGNETISM -EXERCISE-4 (LEVEL-II)
- In the figure shown the wires AB and PQ carry constant currents I(1) a...
Text Solution
|
- In a moving coil galvanometer, torque on the coil can be experessed as...
Text Solution
|
- In a moving coil galvanometer, torque on the coil can be experessed as...
Text Solution
|
- In a moving coil galvanometer, torque on the coil can be experessed as...
Text Solution
|
- In a moving coil galvanometer, torque on the coil can be experessed as...
Text Solution
|
- In a moving coil galvanometer, torque on the coil can be experessed as...
Text Solution
|
- In a moving coil galvanometer, torque on the coil can be experessed as...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite current carrying wire passes through point O and is perpen...
Text Solution
|
- Some laws/processes are given in Column I. Match these with the physic...
Text Solution
|
- A magnetic field vec(B) = B(0)hat(j) , exists in the region a ltxlt2a...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires each carrying a steady current I are shown in four configur...
Text Solution
|
- Statement -1 : The sensitvity of a moving coil galvanometer is increas...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass mand charge q, moving with velocity v enters Region...
Text Solution
|
- A steady current I goes through a wire loop PQR having shape of a righ...
Text Solution
|
- Six point charges , each of the same magnitude q, are arranged in dif...
Text Solution
|
- Electrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, ...
Text Solution
|
- Electrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed po...
Text Solution
|
- An electron and a proton are moving on straight parallel paths with sa...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the field patterns given below is valid for electric field as...
Text Solution
|
- A long insulated copper wire is closely wouind as a spiral of 'N' turn...
Text Solution
|