Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HEAT TRANSFER
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practice Exercise 4.2|8 VideosHEAT TRANSFER
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practice Exercise 4.3|5 VideosHEAT TRANSFER
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Illustrative Example 4.29|1 VideosHEAT AND THERMAL EXPANSION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise UNSOLVED NUMRICAL PROBLEMS FOR PREPARATION OF NSEP, INPhO & IPhO|82 VideosKinetic Theory of Gases and Gas Laws
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Problems for Preparation of NSEP, INPhO & IPhO|64 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-HEAT TRANSFER -Practice Exercise 4.1
- A wall has two layers A and B, each made of different material. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 W heater is placed in a cubical container of edge length 6xx10^(...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a copper rod of length 1.0 m and area of cross-section 10^...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled in a closed cylindrical vessel of 10 cm height and bas...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform steel rod of length 50 cm is insulated on its sides. There i...
Text Solution
|
- Two plates ofthe same area and the same thickness having thermal condu...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows water in a container having 2.0mm thick walls made of a m...
Text Solution
|
- Find the heat current through the frustum of a cone shown in figure-4....
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same me...
Text Solution
|
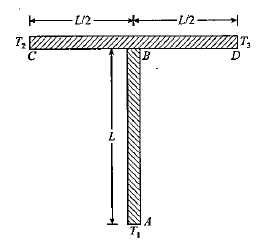
- Two identical rods AB and CD, each of length L are connected as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A room at 20^@C is heated by a heater of resistence 20 ohm connected t...
Text Solution
|