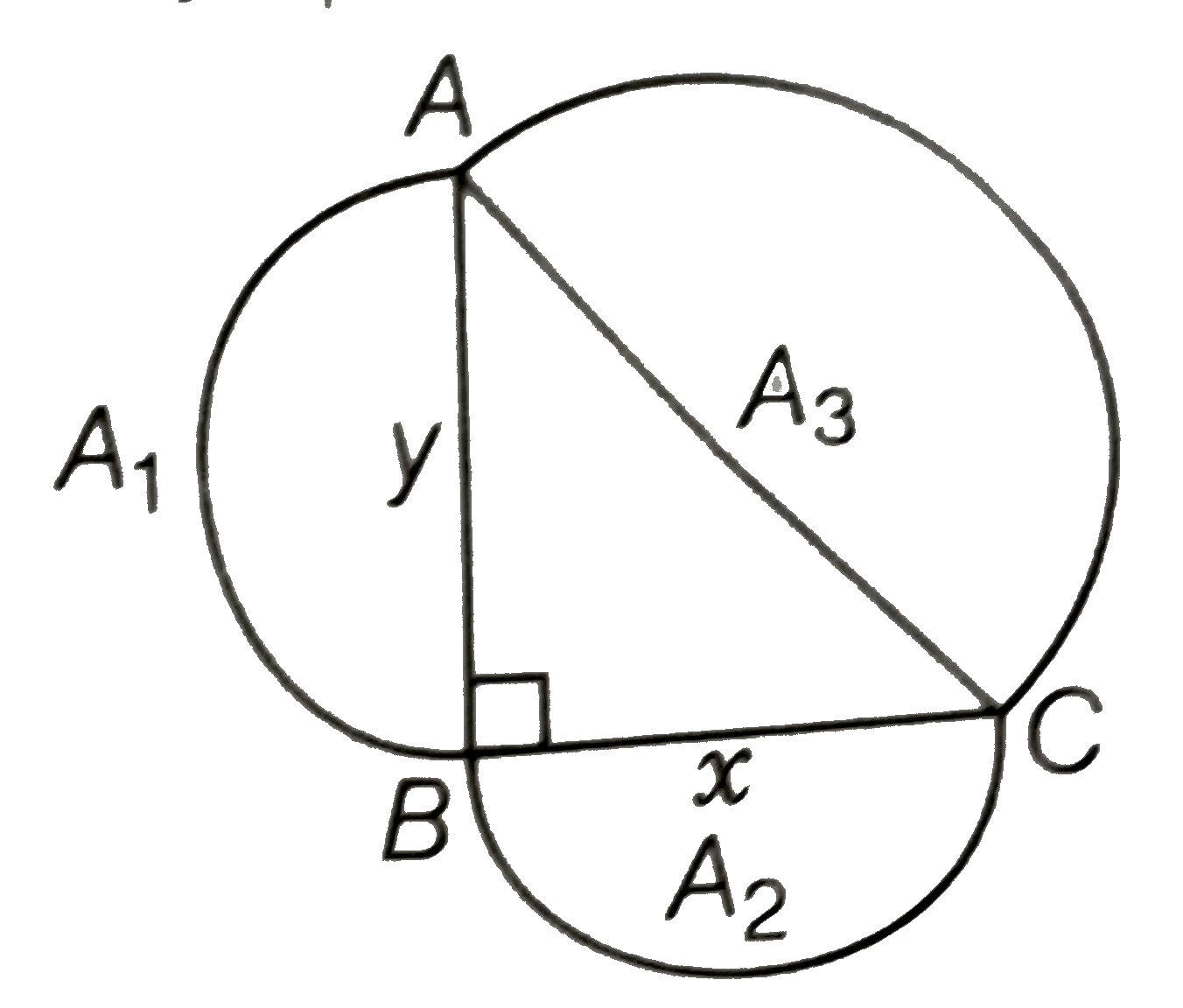Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-TRIANGLES-Triangles
- A 15 high tower casts a sshadow 24 long at a certain time at the same ...
Text Solution
|
- Foot of a 10 m long ladder leaning against a verticle wall is 6 m away...
Text Solution
|
- In given figure, if angleA=angleC, AB= 6 cm, BP = 15 cm, AP = 12 cm an...
Text Solution
|
- It is given that DeltaABC~DeltaEDF such that AB=5 cm, AC=7 cm, DF= 15...
Text Solution
|
- If a line is drawn to one side of a triangle to intersect the other tw...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figures, if PQRS is a parallelogram and ABabs()PS, then p...
Text Solution
|
- A 5 m long ladder is placed leaning towards a vertical wall such that ...
Text Solution
|
- For going to a city B from city A there is a route via city C such tha...
Text Solution
|
- A flag pole 18 m high casts a shadow 9.6 m long. Find the distance of ...
Text Solution
|
- A street light bulb is fixed on a pole 6 m above the level of the stre...
Text Solution
|
- In given figure, ABC is a triangle right angled at B and BDbotAC. If A...
Text Solution
|
- In given figure PQR is a right angled triangle, right angled at Q and ...
Text Solution
|
- Ii DeltaPQR, PDbotQR such that D lies on QR, if PQ=a,PR=b,QD=c and DR=...
Text Solution
|
- In a quadrilateral ABCD, angleA+angleD=90^(@). Prove that AC^(2)+BD^...
Text Solution
|
- In given figure,labs()m and liner segments AB, CD and EF are concurren...
Text Solution
|
- 14 In Fig. 6.21, PA, QB Rc and SD are all perpendiculars to a line l, ...
Text Solution
|
- O is the point of intersection of the diagonals AC and BD of a trapezi...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, line segment DF intersects the side AC of a DeltaABC at the...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that the area of the semicircle drawn on the hypotenuse of a rig...
Text Solution
|
- Equilateral triangles are drawn on the sides of a right triangle. Show...
Text Solution
|