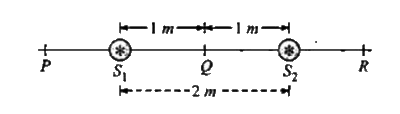Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVES
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practice Exercise 6.1|12 VideosWAVES
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practice Exercise 6.2|11 VideosWAVE OPTICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Problems|28 VideosX-RAYS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerica Problem for Preparation|23 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-WAVES -Unsolved Numerical Problems for Preparation of NSE, INPhO & IPhO
- Two sources S1 " and "S2 separated 2.0 m, vibrate according to equatio...
Text Solution
|
- Write down the equation of a wave travelling in the negative direactio...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the velocity of sound in a gas in which two waves of wavelen...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of sound in hydrogen is 1270 ms^(-1) at temperature T. the s...
Text Solution
|
- When a train is approaching the observer, the frequency of the whistle...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of longitudinal wave is 100 times, then the speed of transve...
Text Solution
|
- A copper wire is held at the two ends by rigid supports. At 30^(@)C, t...
Text Solution
|
- A train approaching a hill at a speed of 40 km//hr sounds a whistle of...
Text Solution
|
- A train approaching a hill at a speed of 40 km//hr sounds a whistle of...
Text Solution
|
- A wave of frequency 500 Hz has a phase velocity of 350 m//s. (a) How f...
Text Solution
|
- A wave of frequency 500 Hz has a phase velocity.of 350 m/s (ii) Wha...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of sound in air at 14^@ C is 340 ms^(-1).What will it be ...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of length 1m, mass 0.1kg and uniform cross-sectional area...
Text Solution
|
- The equation y = A sin 2pi(500t - x//lambda) represents a wave. Speed ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following represents (a) a progressive wave and (b) a sta...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of sound in hydrogen is 1270 m s^(-1) at 0^(@)C and the f...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperature is the velocity of sound in nitrogen equal to its ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the velocity of sound in a mixture of two gases obtained by ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the velocity of sound in a mixture of two gases obtained by ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the frequency of a ntoe emitted by a wire 20cm in length whe...
Text Solution
|
- In the spectrum of light of a luminous heavenly body the wavelength of...
Text Solution
|