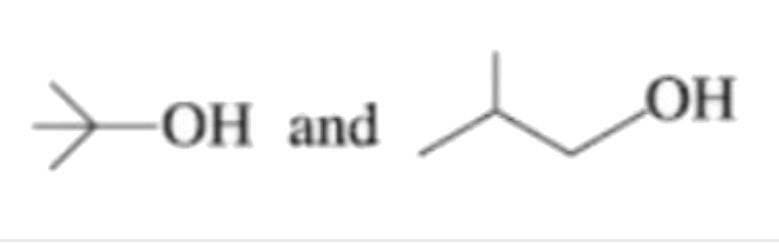
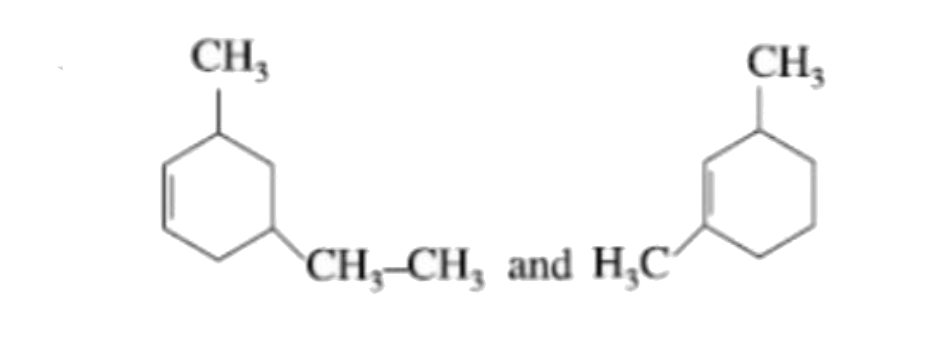A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA JEE MOCK TEST 33-CHEMISTRY
- Assume 100% ionisation of the following aq. Solution of (I) [Pt(NH(3...
Text Solution
|
- During an electrolysis of conc. H(2)SO(4), peroxydisulphuric acid (H(2...
Text Solution
|
- 1 M NH(4)OH and 1 M HCl are mixed to make a total volume of 300 mL. If...
Text Solution
|
- Which are not position isomers?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has highest K(a) value?
Text Solution
|
- Which of following reagents does not give isobutane when reacted with ...
Text Solution
|
- The final product obtained in the reaction
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will not be formed when calcium formate is dist...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following chemicals can be added for sweetening of food i...
Text Solution
|
- C(4)H(7)OCl overset(NH(3))rarr C(4)H(9)ON underset(KOH)overset(Br(2))r...
Text Solution
|
- What is the simplest formula of a solid whose unit cell has the atom A...
Text Solution
|
- 0.1 M KMnO(4) is used for the following titration. What volume of the ...
Text Solution
|
- CO(2) gas is liquefaction for 1 mole of CO(2). Then which stateme...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement about anhydrous aluminium chloride is...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following is the correct statement?
Text Solution
|
- A solution containing 10 g of a non- voltile, higher nonelectrolyte an...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction 3AhArr C+2D, initially A was taken. At equilibrium th...
Text Solution
|
- How many of the following are polar aprotic solvents?
Text Solution
|
- How many Cr-O bonds are equivalent in chromate dianion ?
Text Solution
|
- 5 ml As(2)S(3) is mixed with distilled water and 0.01 M solution of an...
Text Solution
|