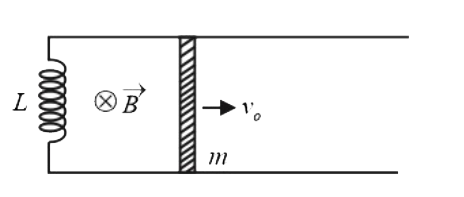
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA JEE MOCK TEST 39-PHYSICS
- The horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 3.6 xx 10^(-...
Text Solution
|
- Two copper spheres of the same radii one hollow and the other solid ar...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in figure, the two parallel conducting rails, in a horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- In the given diagram, there is a conducting sphere of radius r which i...
Text Solution
|
- Two stars of masses 3 xx 10^(31) kg each, and at distance 2 xx 10^(11)...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of a liquid drops from 365 K to 361 K in 2 minutes . ...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron, a proton , and an electron and an alpha particle enter a re...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m =2 kg is placed on a plank of mass M = 10 kg, which ...
Text Solution
|
- Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio 8 : 125. What is the ratio o...
Text Solution
|
- An object of mass 1kg executes simple harmonic oscillations along the ...
Text Solution
|
- A "50 W m"^(-2) energy density of sunlight is incident normally on the...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden block of mass 1kg and density 800 Kg m^(-3) is held stationer...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent cube of side d, made of a material of refractive index ...
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral prism of mass m rests on a rough horizontal surface wit...
Text Solution
|
- A Zener diode with a breakdown voltage of 4 V is connceted in sereis w...
Text Solution
|
- The dimensins of a/b in the equation P=(a-t^(2))/(bx) where P is press...
Text Solution
|
- An unpolarized light of intensity I(0) passes through three polarizers...
Text Solution
|
- A wall is moving with velocity u and a source of sound moves with velo...
Text Solution
|
- In a resonance tube experiment to determine the speed of sound in air,...
Text Solution
|
- The main scale of a vernier calliper reads in mm and its vernier scale...
Text Solution
|