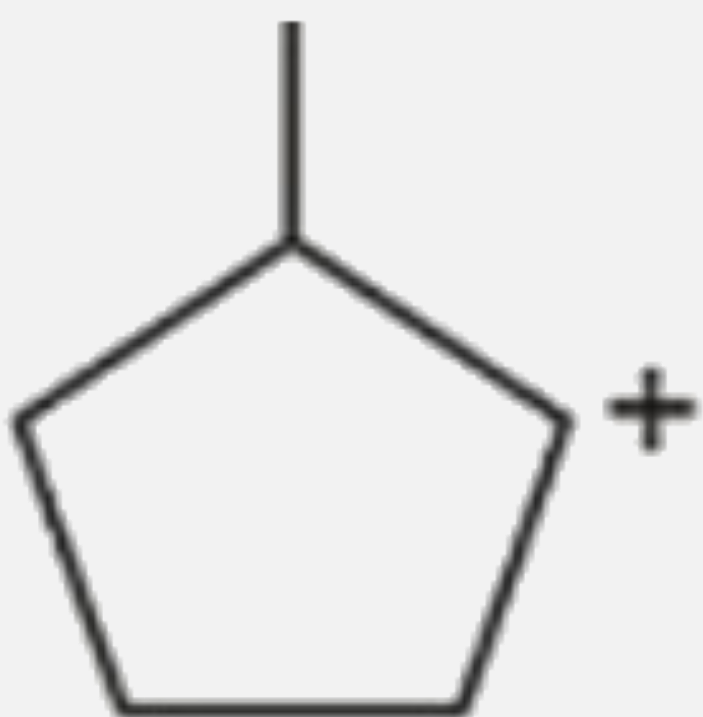
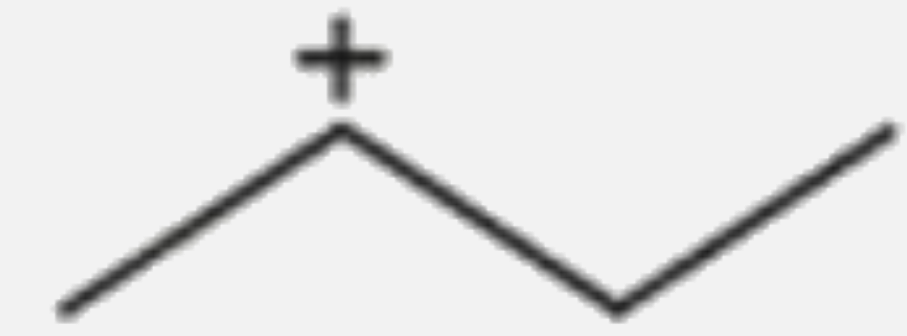
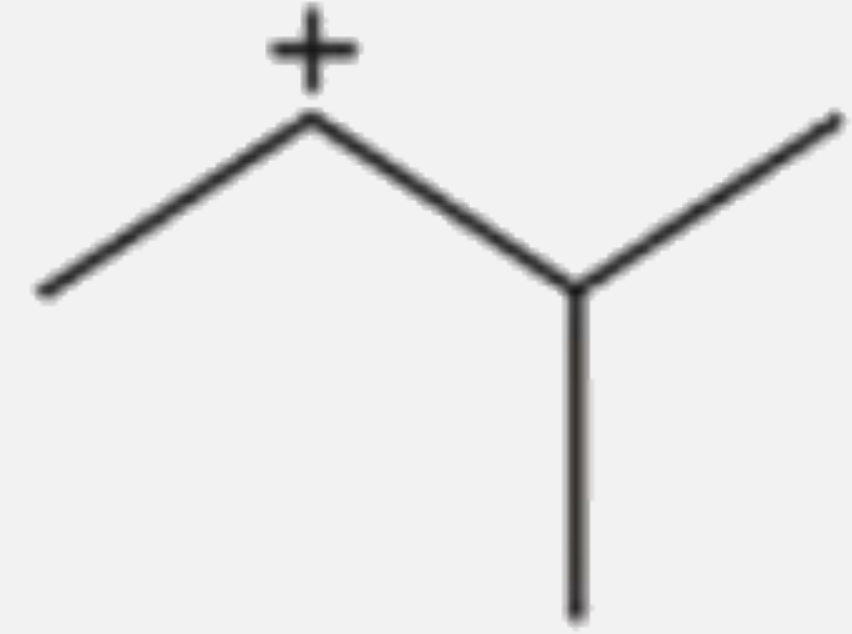
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA NEET SET 57-CHEMISTRY
- the study of action of drag is know as
Text Solution
|
- Molecular size of ICI and Br2 is nearly same but boiling point of ICI...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbocations would not likely rearrange to more...
Text Solution
|
- Which reaction does hydroquinone undergo most readily ?
Text Solution
|
- Ethyl alcohol on oxidation with acidified K(2)Cr(2)O(7) gives
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass 40"g mol"^(-1)...
Text Solution
|
- Oxidising power of chlorine in aqueous solution can be determined by t...
Text Solution
|
- The rate law for the chemical reaction 2NO2Cl rarr 2NO2 +Cl2 + Cl2 = k...
Text Solution
|
- The hybridisation of atomic orbitals of nitrogen in NO2^+ , NO3^- and...
Text Solution
|
- Hard water can block radiators due to the formation of
Text Solution
|
- When two moles of hydrogen expands isothermally against a constant pre...
Text Solution
|
- When mercuric iodide is added to the aqueous solution of potassium iod...
Text Solution
|
- At CMC, the surfactant molecules :
Text Solution
|
- Reaction : 2Fe^(3+)+3I^(-) hArr 2Fe^(2+) + I3^(-) The standard reducti...
Text Solution
|
- The first and second dissociation constant of an acid H(2)A are 1.0xx1...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has the highest molar conductivity in solution?
Text Solution
|
- X reacts with dilute nitric acid to form 'laughing gas' . What is X ?
Text Solution
|
- In case of condensation of polymers ?
Text Solution
|
- How many octahedral and tetrahedral holes are present per unit cell in...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbohydrate is a reducing sugar ?
Text Solution
|