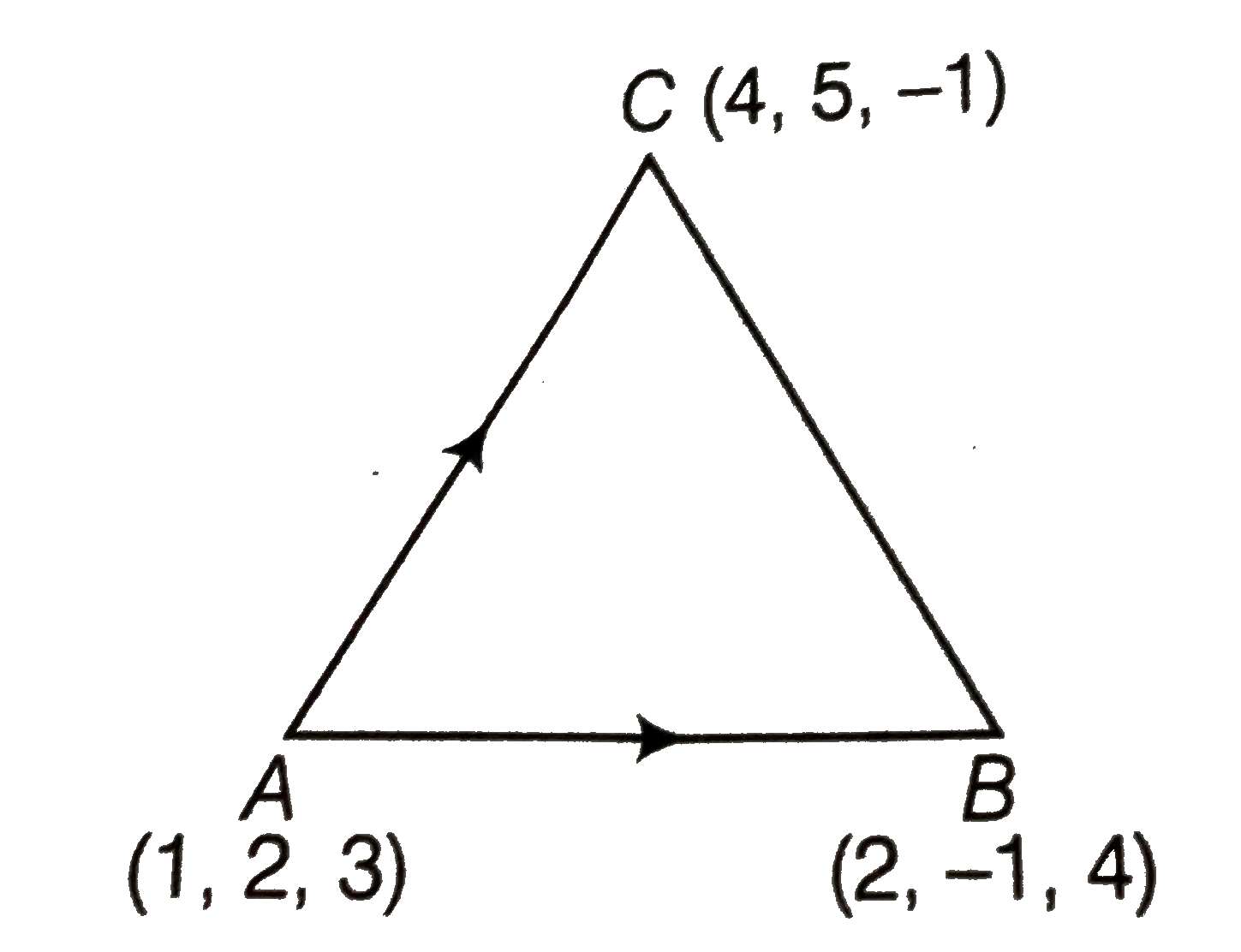Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-VECTOR ALGEBRA-Vector Algebra
- Find the sine of the angle between the vectors veca=3hati+hatj+2hatkan...
Text Solution
|
- If A, B, C and D are the points with position vectors hati-hatj+hatk,2...
Text Solution
|
- Using vectors, find the area of the DeltaABC with vertices A(1, 2, 3),...
Text Solution
|
- Using vectors, prove that the parallelogram on the same base and betwe...
Text Solution
|
- (Cosine Formulae) if a ,b ,c are the lengths of the sides opposite res...
Text Solution
|
- If veca,vecbandvecc determine the vertices of a triangle, show that (1...
Text Solution
|
- Show that area of the parallelogram whose diagonals are given by veca ...
Text Solution
|
- If veca=hati+hatj+hatk and vecb=hatj-hatk find a vector vecc such that...
Text Solution
|
- The vector in the direction of the vector hati-2hatj+2hatk that has ma...
Text Solution
|
- The position vector of the point which divides the join of points 2vec...
Text Solution
|
- The vector having initial and terminal points as (2, 5, 0) and (-3,7,4...
Text Solution
|
- The angle between two vectros vecaandvecb with magnitudes sqrt3 and 4,...
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of lamda such that the vectors veca=2hati+lamdahatj+hat...
Text Solution
|
- The value of lamda for which the vectors 3hati-6hatj+hatkand2hati-4hat...
Text Solution
|
- The vectors from origin to the points A and B are veca=2hati-3hatj+2ha...
Text Solution
|
- For any vector veca the value of |vecaxxhati|^2+|vecaxxhatj|^2+|vecaxx...
Text Solution
|
- If |veca|=10,|vecb|=2andveca.vecb=12, then the value of |vecaxxvecb| i...
Text Solution
|
- The vectors lamdahati+hatj+2hatk,hati+lamdahatj-hatkand2hati-hatj+lamd...
Text Solution
|
- If veca,vecbandvecc are unit vectors such that veca+vecb+vecc=0, then ...
Text Solution
|
- The projection vector of veca" on "vecb is
Text Solution
|