A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-WAVE OPTICS-Wave Optics
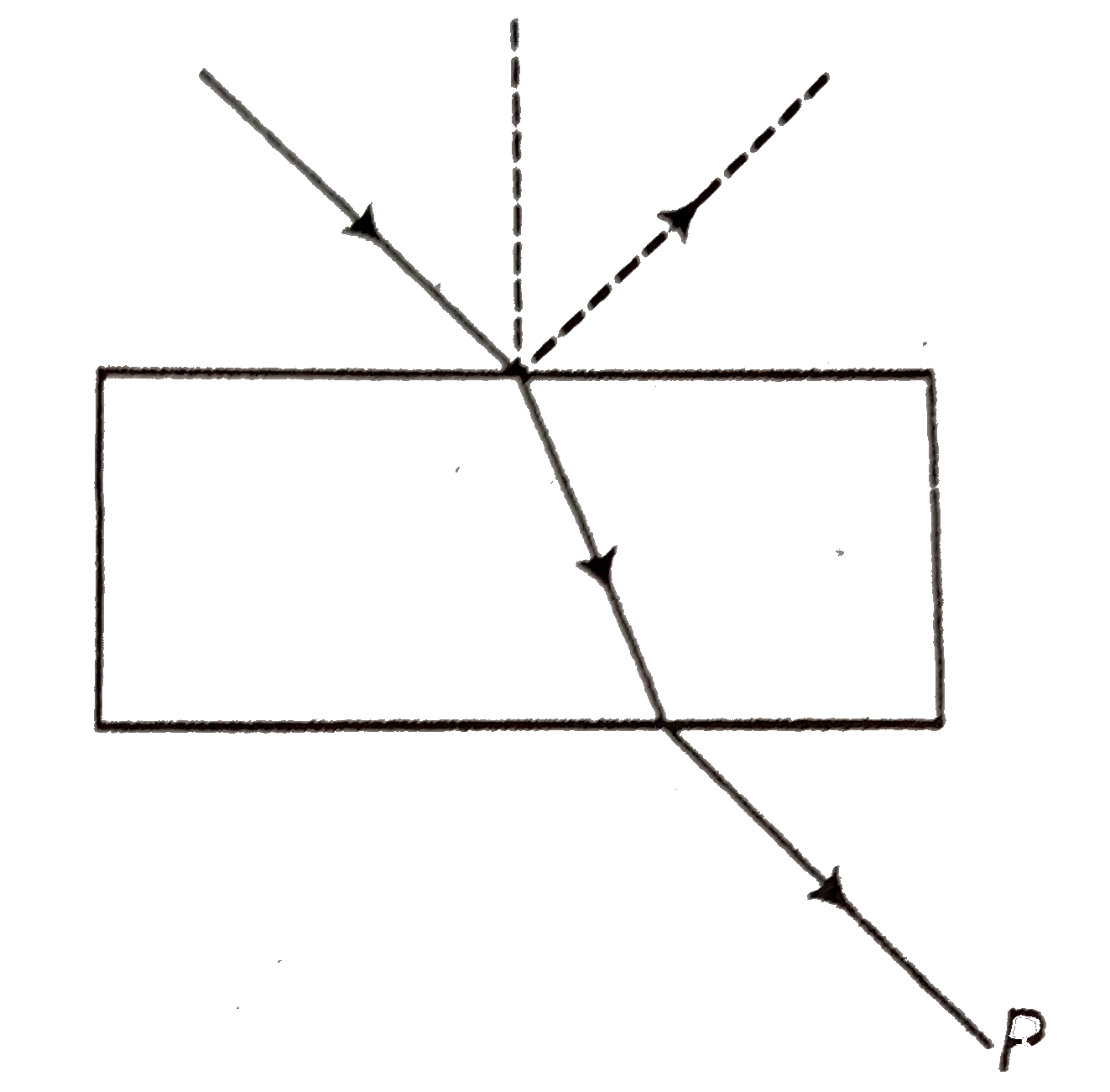
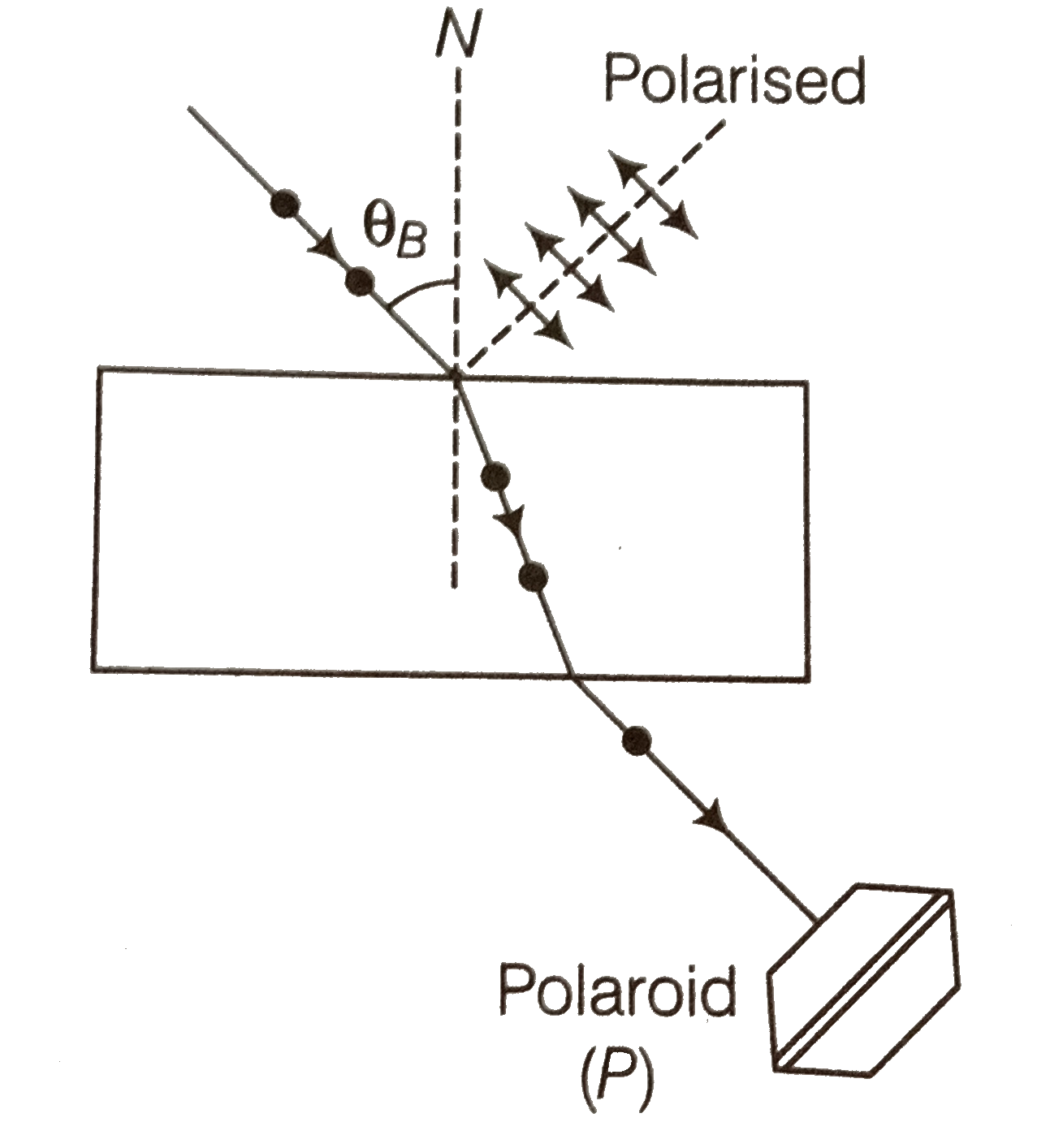
- Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster's ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 10^(4) Å . The image see...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a ray of light incident from air onto a slab of glass (refrac...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, the source is white light. One of...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a standard two slit arrangement with slits S(1), S(2). P(...
Text Solution
|
- Two source S(1) and S(2) of intensity I(1) and I(2) are placed in fron...
Text Solution
|
- Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 10^(3)Å. The image of...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of t...
Text Solution
|
- For light diverging from a point source
Text Solution
|
- Is Huygen's principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
Text Solution
|
- Consider a point at the focal point of a convex lens. Another convex l...
Text Solution
|
- What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight ?
Text Solution
|
- Why is the diffraction of sound wave more evident in daily experience ...
Text Solution
|
- The human eye has an approximate angular resolution of phi = 5.8xx10^(...
Text Solution
|
- A polariod (I) is placed infront of a monochromatic source. Another p...
Text Solution
|
- Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is inciden...
Text Solution
|
- For the same objective, the ratio of least separation between two poin...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a two slit interference arrangements (figure) such that the d...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolar...
Text Solution
|
- A small transparent slab containing material of mu=1.5 is placed along...
Text Solution
|