Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES-Application Of Derivatives
- Find the dimensions of the rectangle of perimeter 36cm which will s...
Text Solution
|
- The sum of the surface areas of a sphere and a cube is given. Show tha...
Text Solution
|
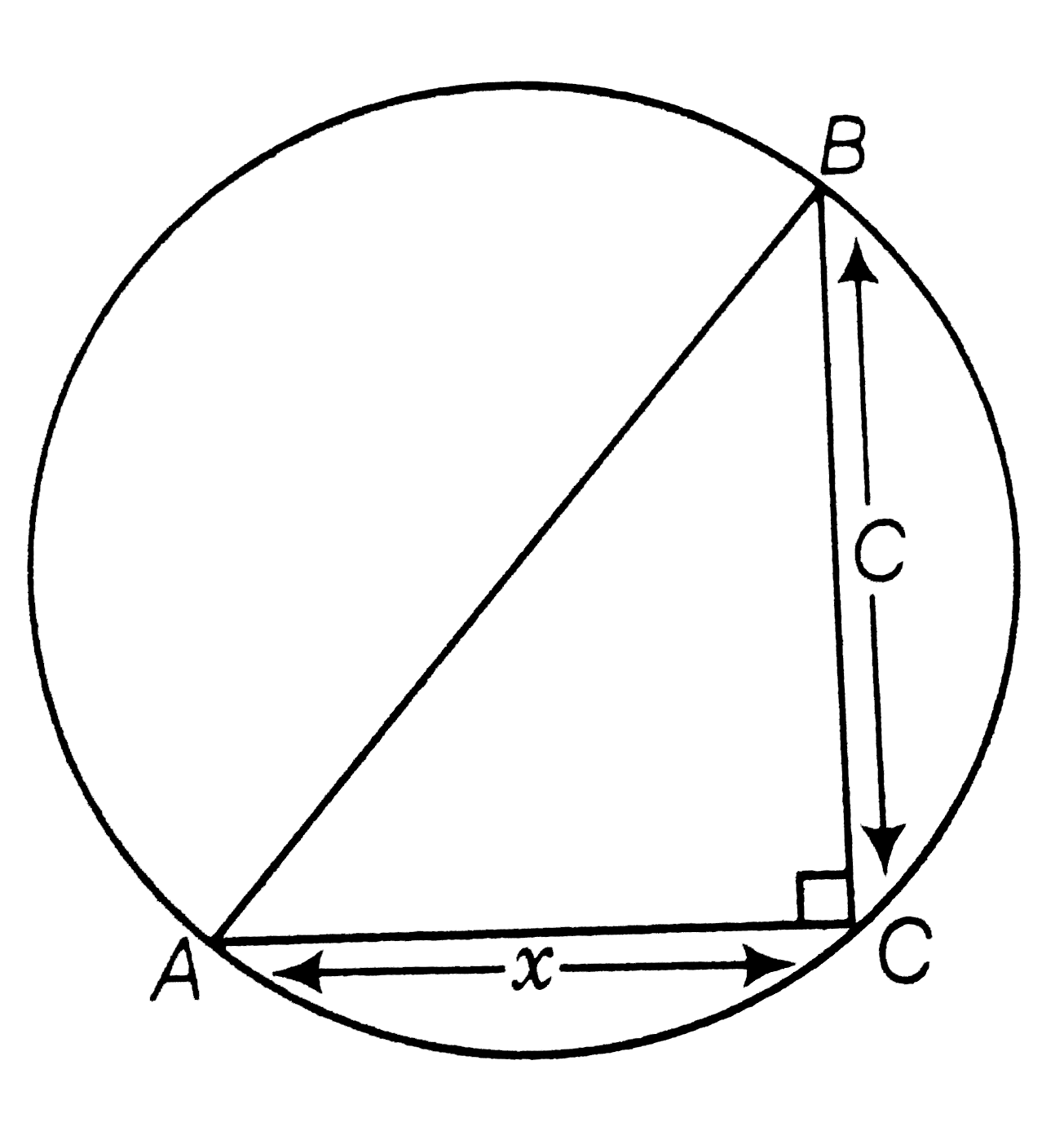
- A B is a diameter of a circle and C is any point on the circle. ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal box with a square base and vertical sides is to contain 102...
Text Solution
|
- The sum of the surface areas of the rectangular parallelopiped with...
Text Solution
|
- The sides of an equilateral triangle are increasing at the rate of ...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder 5 m long is leaning against a wall. The bottom of the ladder ...
Text Solution
|
- The curve y= x^(1/5) has at (0, 0)
Text Solution
|
- Find the equation(s) of normal(s) to the curve 3x^2-y^2=8 which is (ar...
Text Solution
|
- If the curves ay+x^2=7 and x^3=y cut orthogonally at (1, 1) then a= ...
Text Solution
|
- If y=x^4-12 and if x changes from 2 to 1.99. what is the appoinmate ch...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equation of the tangent to the curve (1+x^2)y=2-x , where it ...
Text Solution
|
- The points at which the tangents to the curve y=x^(3)-12x+18 are paral...
Text Solution
|
- The tangent to the curve y=e^(2x) at the point (0,1) meets X-axis at
Text Solution
|
- The slope of the tangent to the curve x=t^2+3t-8,y=2t^2-2t-5at the po...
Text Solution
|
- The two curves x^3-3xy^2+2=0 and 3x^2y-y^3-2=0
Text Solution
|
- 24. Find the intervals in which the following function is (a) increasi...
Text Solution
|
- The function f:R rarr R be defined by f(x)=2x+cosx then f
Text Solution
|
- If y=x(x-3)^(2) decreases for the values of x given by
Text Solution
|
- The function f(x) =4sin^(3)x-6sin^(2)x +12 sinx + 100 is strictly
Text Solution
|