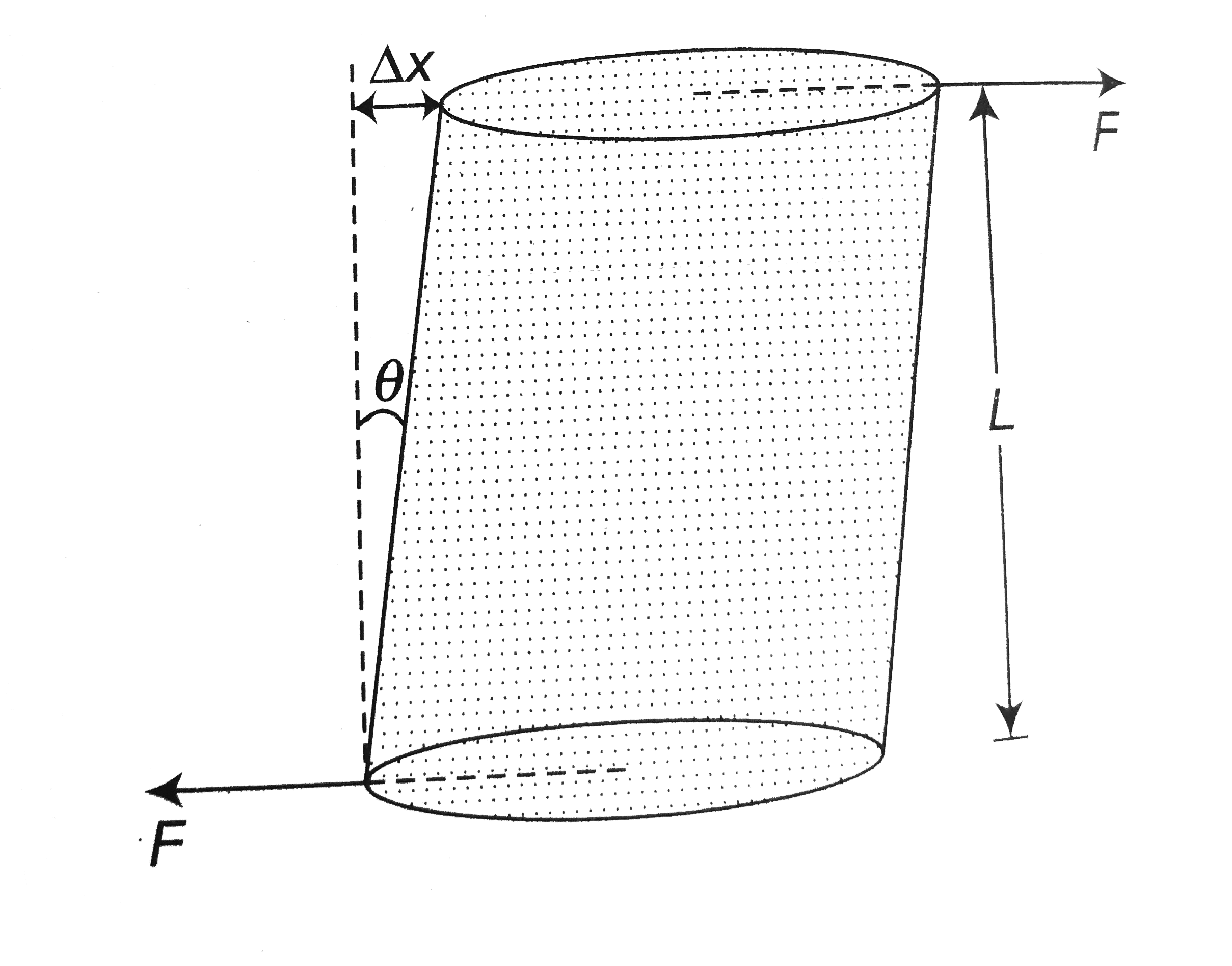
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Hooke'S Law|3 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Stress-Strain Curve|5 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Elastic Behavior Of Solids|2 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS-Stress And Strain
- Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Text Solution
|
- Shear stress is related to
Text Solution
|
- If the volume of a wire remains constant when subjected to tensile str...
Text Solution
|
- Fluids can develop
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is correct regarding poissen's ratio...
Text Solution
|
- If two equal and opposite deforming forces are applied parallel to the...
Text Solution
|
- Stress is aquantity.
Text Solution
|
- The breaking stress of a wire depends on
Text Solution
|
- A wire is suspended from the ceiling and stretched under the action of...
Text Solution
|