A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|8 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Applications Of Elastic Behaviour Of Materials|8 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS-Higher Order Thinking Skills
- A steel bar ABCD 40 cm long is made up of three parts AB, BC and CD, ...
Text Solution
|
- Three elastic wires PQ, PR and PS support a body P of mass M, as shown...
Text Solution
|
- The adjacent graph shows the extension Deltal of a wire of length 1m...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius R made of a material of bulk modulus K is sur...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a horizontal thick copper wire of length 2L and radius 2R i...
Text Solution
|
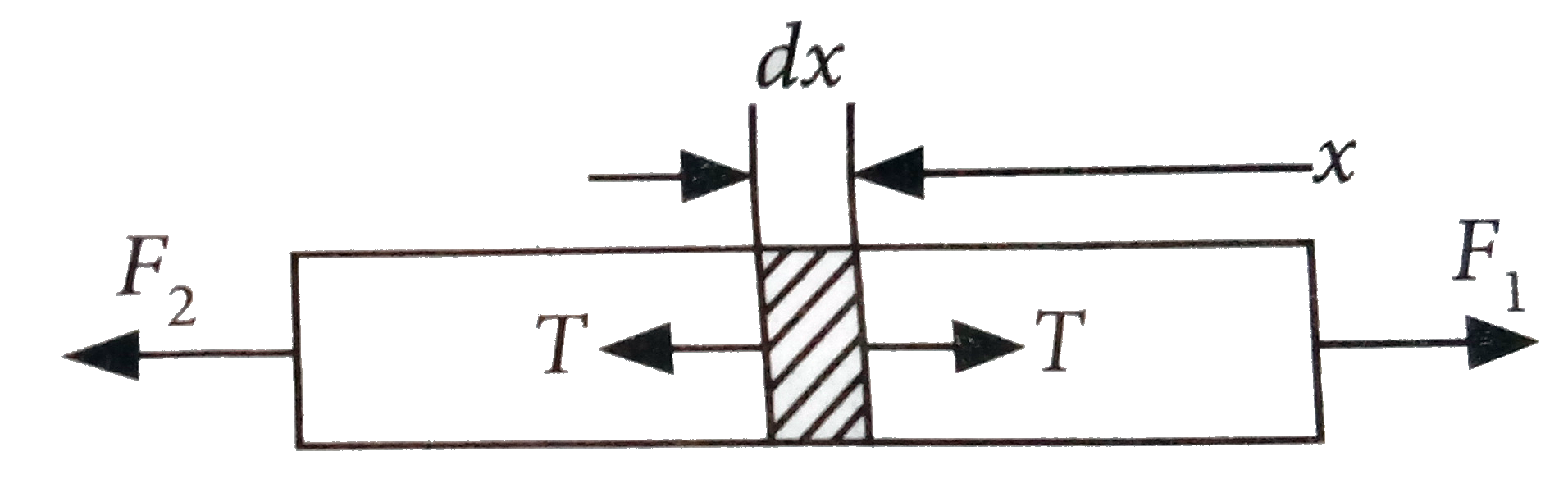
- Two opposite forcesF(1) = 120 N and F(2) = 80 N act on an elastic plan...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 1 kg and 2 kg are connected by a metal wire going...
Text Solution
|
- Three equal masses 3 kg are connected by massless string of cross sect...
Text Solution
|