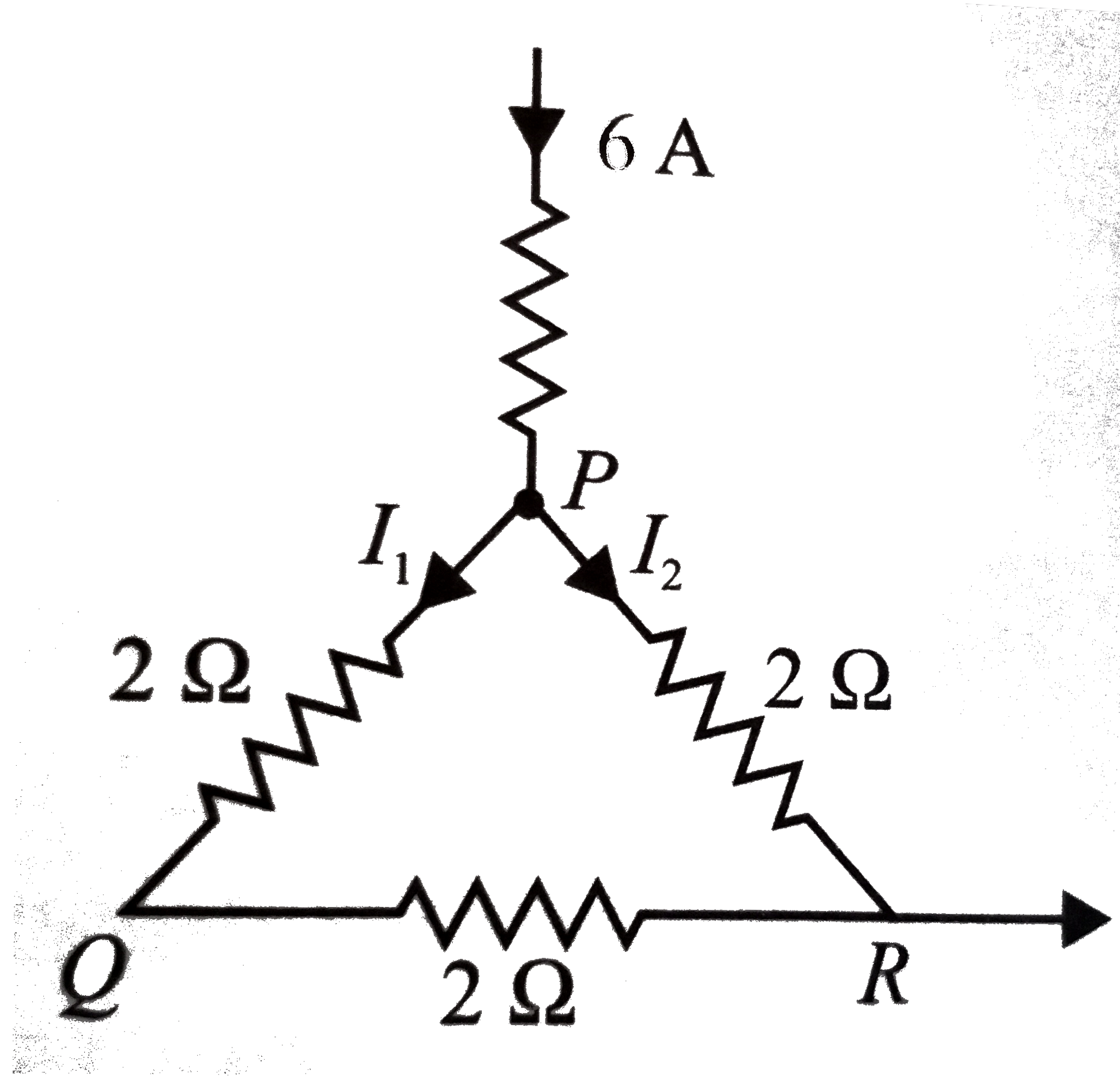A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Wheatstone Bridge|6 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Meter Bridge|4 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Cell In Series And In Parallel|3 VideosCOMMUNITCATION SYSTEMS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise HOTS|10 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-Kirchoff'S Law
- Point out the right statements about the validity of, Kirchhoff's junc...
Text Solution
|
- The figure below shows current in a part of electric circuit. The curr...
Text Solution
|
- A circuit has a section ABC if the potential at point A,B and C are V(...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference between A and B as shown in figure is
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit the potential at point B is zero, the potential a...
Text Solution
|
- A current of 6 A enters one corner P of an equilateral triangle PQR ha...
Text Solution
|
- 7 V battery with internal resistance 2Omega and 3V battery with intern...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, the value of currents I(1), I(2) and I(3) are
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in figure the current flowing through 25 V cell i...
Text Solution
|
- A battery, an open switch and a resistor are connected in series as sh...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells e(1) and e(2) connected in opposition to each other as shown...
Text Solution
|