A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVE OPTICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|5 VideosWAVE OPTICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosWAVE OPTICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Polarisation|18 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS : MATERIALS , DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS-WAVE OPTICS-Higher Order Thinking Skills
- Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolar...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths 650 nm and 520 nm is use...
Text Solution
|
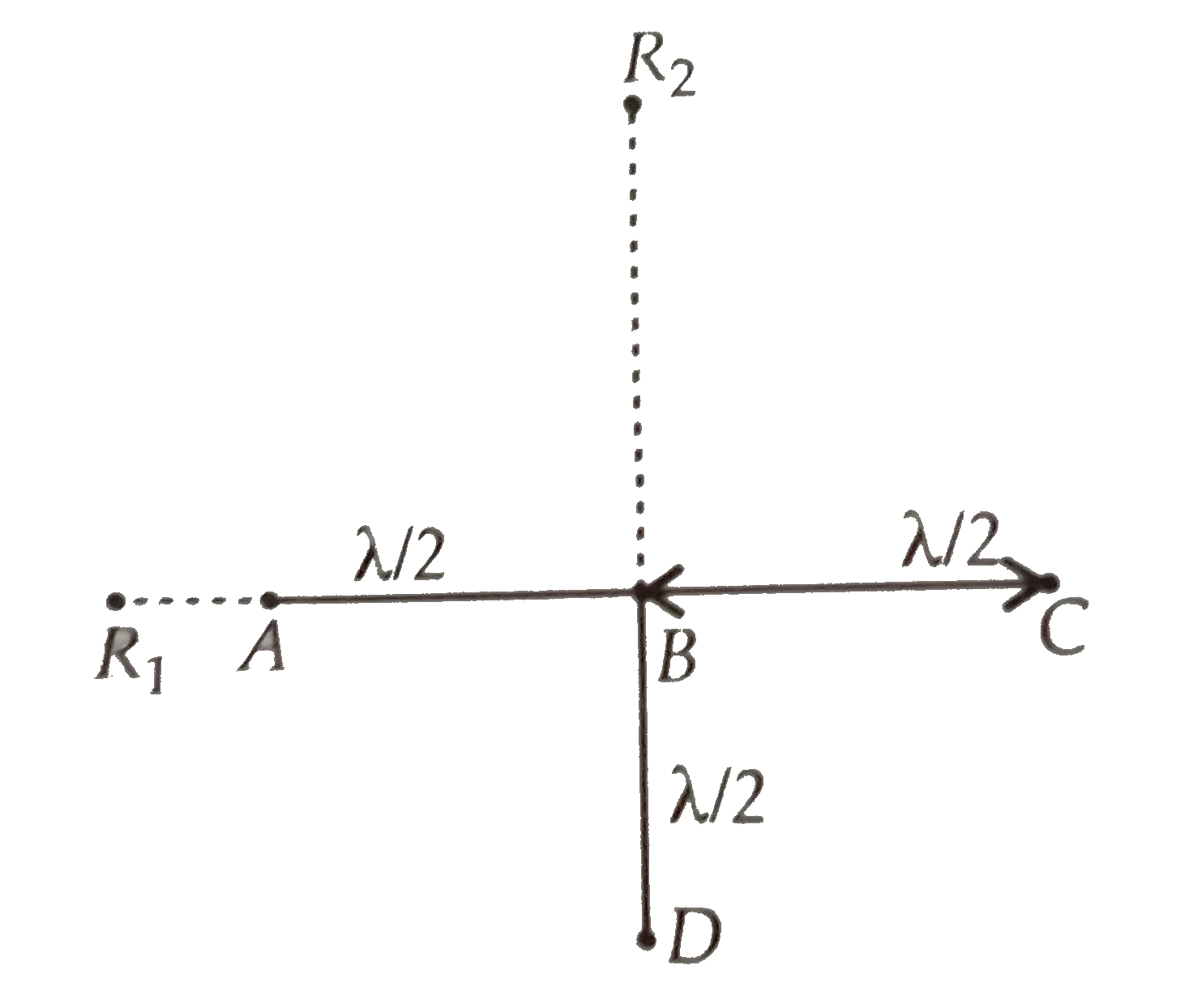
- Four identical monochromatic sources A,B,C,D as shown in the (figure) ...
Text Solution
|
- In question number 3, which of the two receivers picks up the larger s...
Text Solution
|
- In question number 3, which of the two receivers picks up the larger s...
Text Solution
|
- To ensure almost 100% transmittivity, photographic lenses are often co...
Text Solution
|
- Two points nonochromatic and coherent sources of light of wavelength l...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a two slit interference arrangements (figure) such that the d...
Text Solution
|