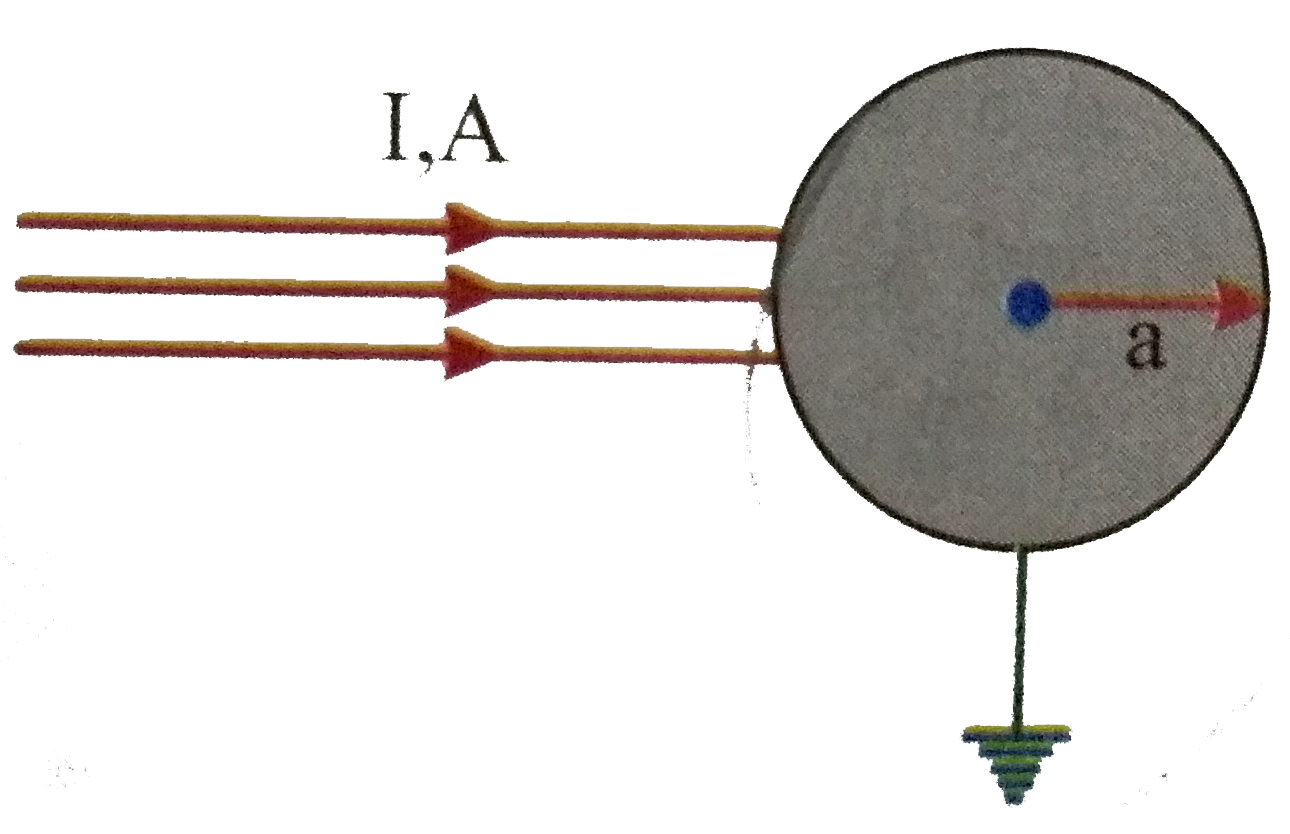
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|8 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Davisson And Germer Experiment|3 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS-DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER -Higher Order Thinking Skills
- (a) Estimate the speed with which electrons emitted from a heated cath...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles A and B of de-broglie wavelength lambda(1) and lambda(2)...
Text Solution
|
- A silver of radius 1 cm and work function 4.7 eV is suspended from an ...
Text Solution
|
- A proton is fired from very far away towards a nucleus with charge Q ...
Text Solution
|
- Two metallic plates A and B , each of area 5 xx 10m are placed paralle...
Text Solution
|
- In question number 5, find the kinetic energy of the most energetic ph...
Text Solution
|
- When a beam of 10.6 eV photons of intensity 2.0 W //m^2 falls on a pla...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of monochromatic radiation of cross-section area A(lt ...
Text Solution
|