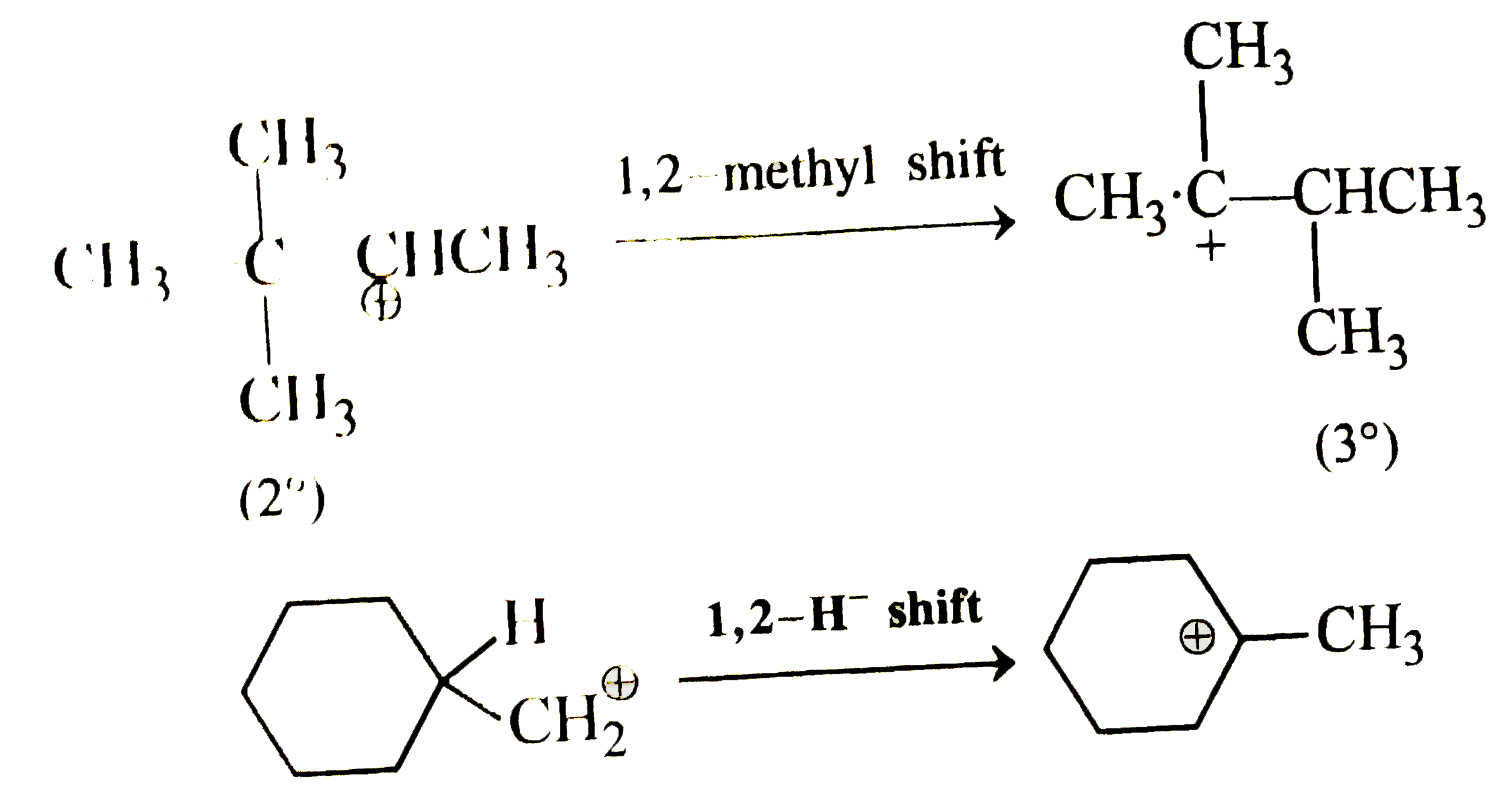
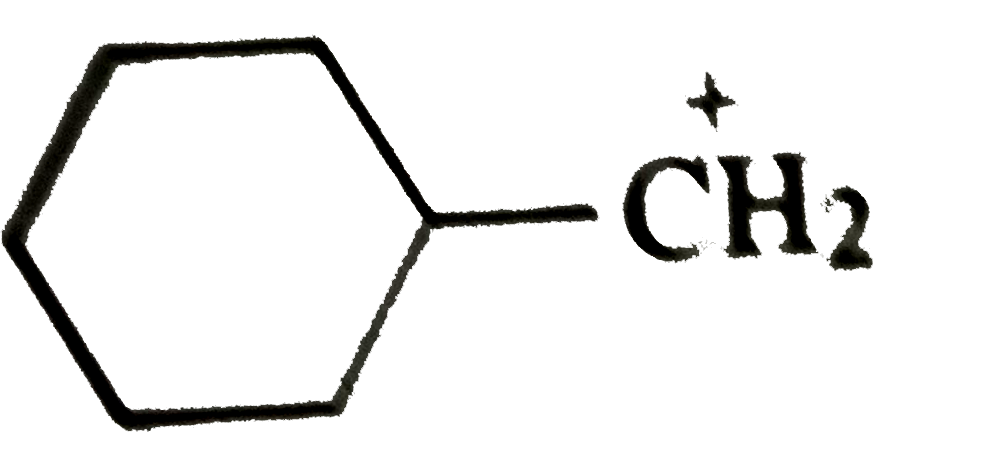
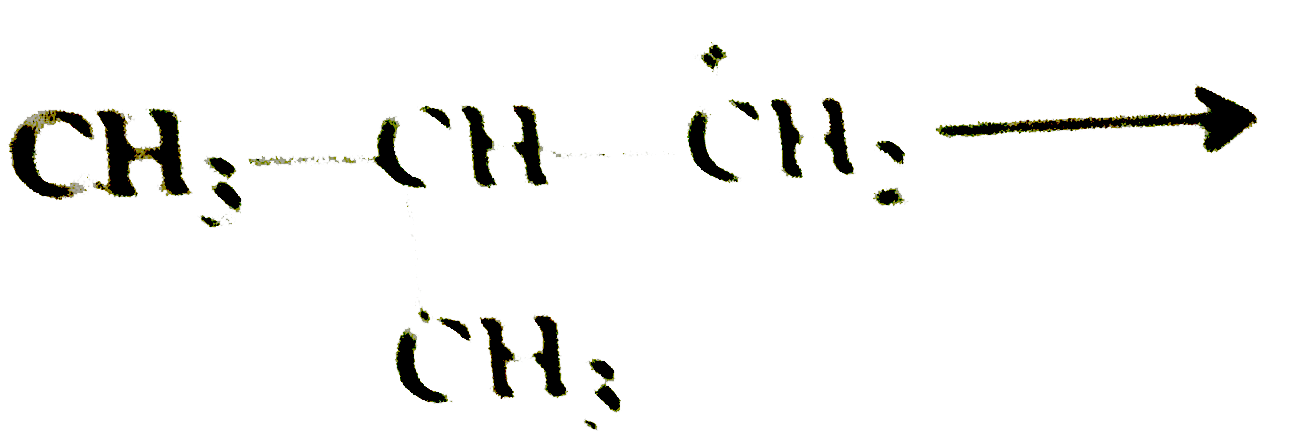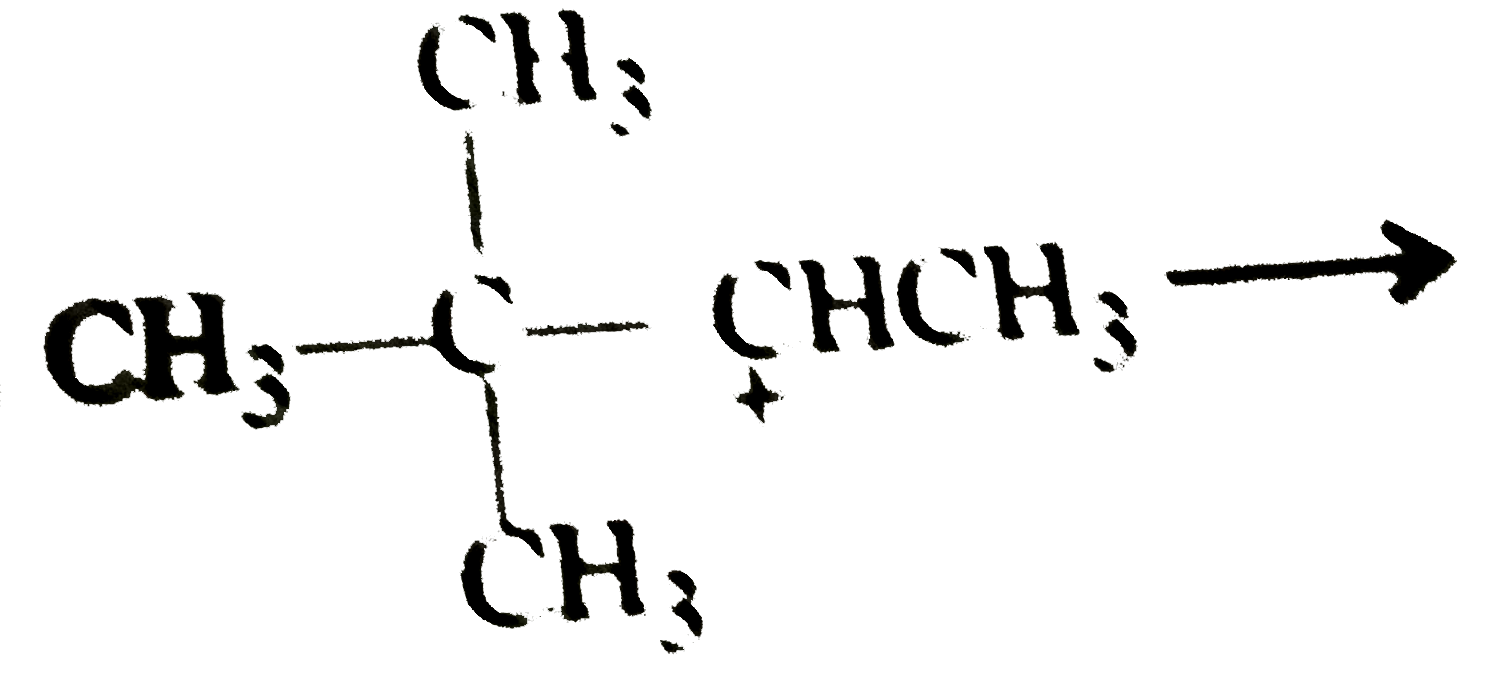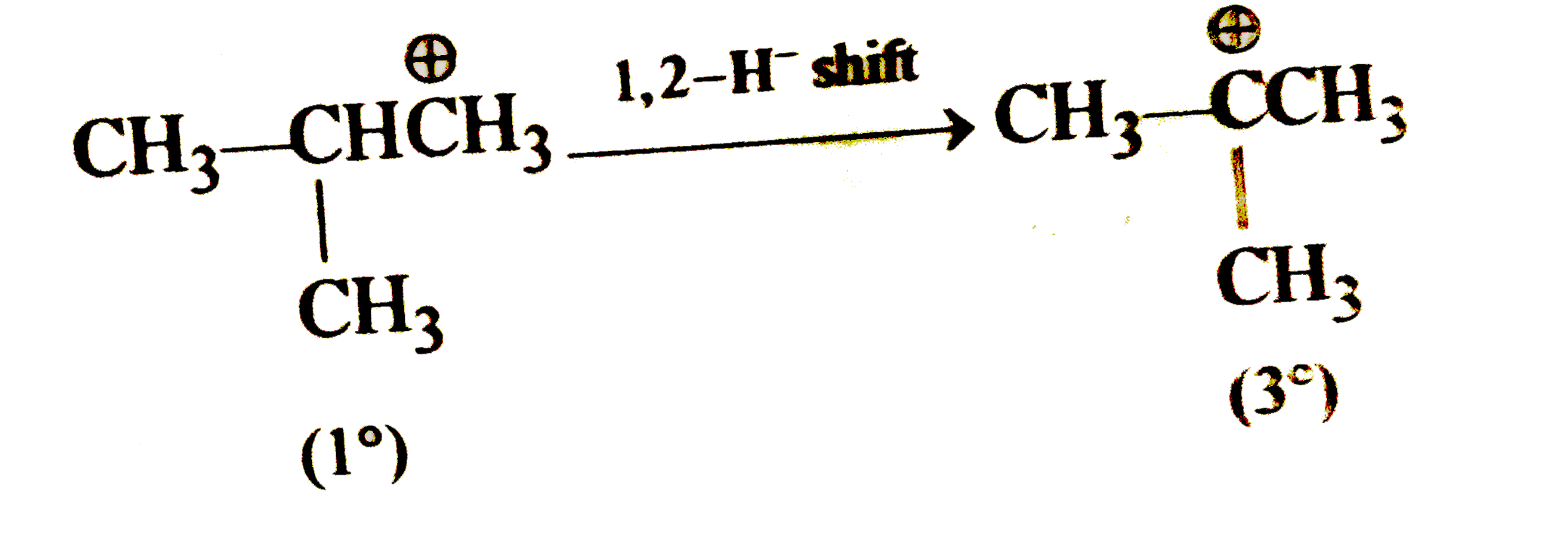A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise REASON ASSERTION TYPE MCQS|12 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise ULTIMATE PREPARATORY PACKAGE|51 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise SELECTED STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE MCQS|64 VideosALKALI EARTH METALS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit test-12|5 VideosBIOMOLECULES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise MATRIX - MATCH TYPE|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE MCQS
- Organic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon...
Text Solution
|
- Organic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon...
Text Solution
|
- Organic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon...
Text Solution
|
- Organic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon...
Text Solution
|
- Organic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon...
Text Solution
|
- Organic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon...
Text Solution
|
- Organic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of an electrophile with a nucleophile is the same as the ...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of an electrophile with a nucleophile is the same as the ...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of an electrophile with a nucleophile is the same as the ...
Text Solution
|