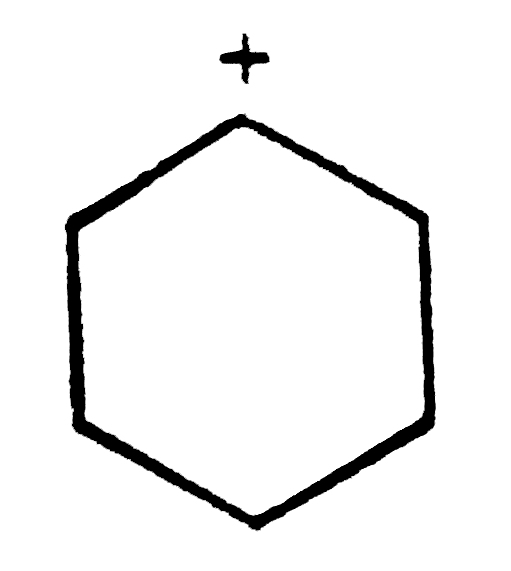
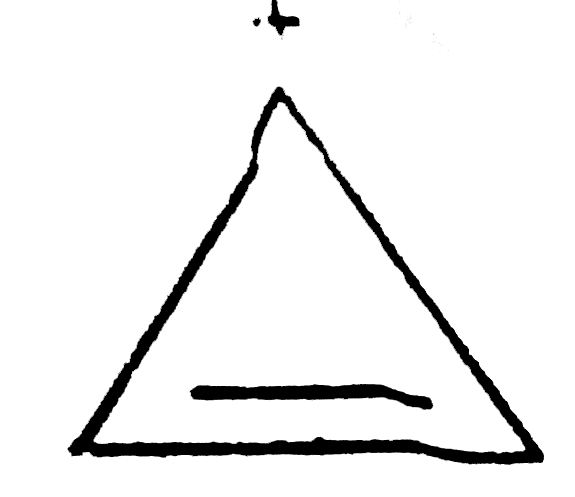
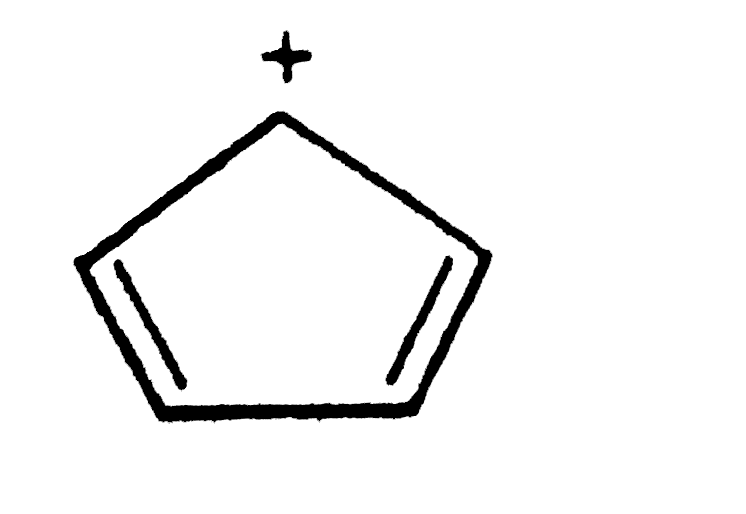
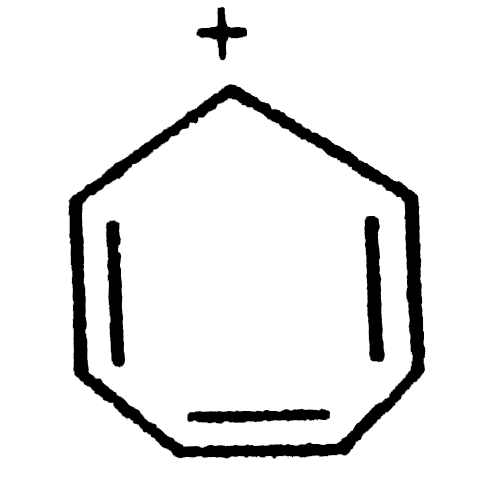
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Matrix Type Questions|2 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise REASON ASSERTION TYPE MCQS|12 VideosALKALI EARTH METALS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit test-12|5 VideosBIOMOLECULES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise MATRIX - MATCH TYPE|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-ULTIMATE PREPARATORY PACKAGE
- Which of the following can act both as an electrophile and a nucleophi...
Text Solution
|
- In Hoffinann bromamide reaction, the reactive intermediate involved is...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following can act as an electrophile ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is correct ?
Text Solution
|
- The - I effect of -NO(2),-CN,-COOH,-Cl decreases in the order
Text Solution
|
- The + I effect of (CH(3))(3)C-(I), CH(3))(2)CH-(II), CH(3)CH(2)- (III)...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following free radicals in order of stability underset(I...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following free radicals in order of stability underset(I...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following carbonium ions in order of decreasing stability ...
Text Solution
|
- The inductive effect of the alkyl groups on a saturated carbon chain f...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is most stable alkene ?
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following has inductive, mesomeric and hyperconjugati...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following alkenes : 1. H(2)C=C(CH(2)CH(3))CH(CH(3))(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following compounds would have the highest heat of hy...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is most stable alkene ?
Text Solution
|
- The less stable carbocation rearranges to more stable carbocation ion....
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing order of the stability of the ions underset((I))under...
Text Solution
|
- In but-1, 3-diene the C(2)-C(3) bond length is
Text Solution
|
- The most stable carbocation is
Text Solution
|
- A solution of ( + )-1-chloro-1-phenylethane in t toluene racemises slo...
Text Solution
|