A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-MOTION IN A PLANE-(C )Medical entrances gallery
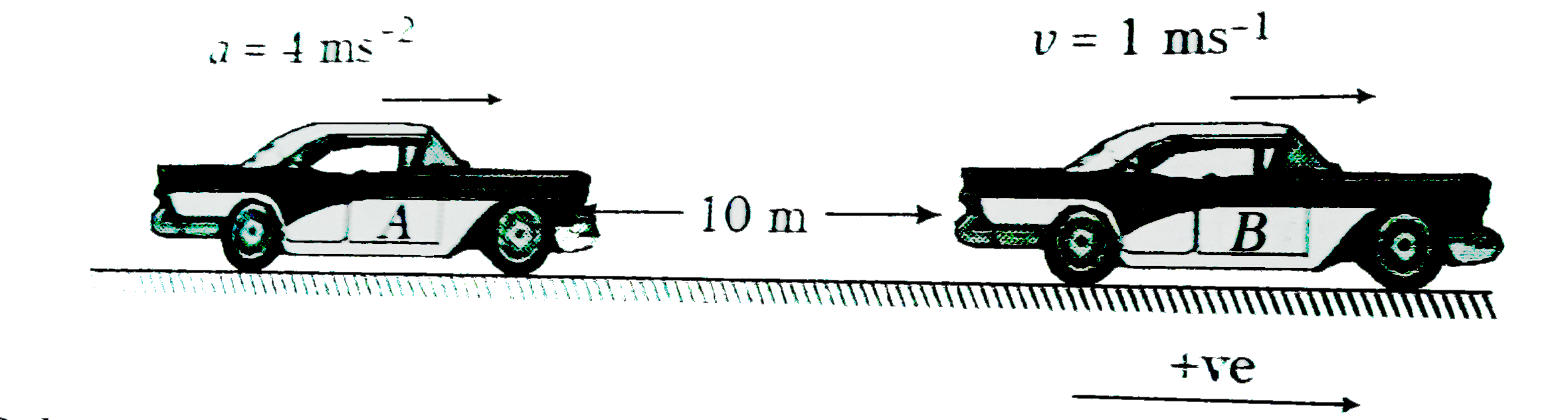
- Car A and car B start moving simultaneously in the same direction alon...
Text Solution
|
- If the velocity of a particle is v = At + Bt^2, where A and B are cons...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of unit mass undergoes one-dimensional motion such that its...
Text Solution
|
- The ball is dropped from a bridge 122.5 m above a river, After the ba...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the ground with a speed of 25...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in an XY-plane in such a way that its x and y-coordin...
Text Solution
|
- A point moving with constant acceleration from A to B in the straight ...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement-time graph of a particle is as shown below. It indica...
Text Solution
|
- A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly to a speed of 180 kmh...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity - time graph for two bodies A and B are shown in figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving such that its position coordinates (x, y) are (2m...
Text Solution
|
- A ball thrown vertically upwards after reaching a maximum height h ret...
Text Solution
|
- A police jeep is chasing with, velocity of 45 km//h a thief in another...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves with constant acceleration along a straight line stre...
Text Solution
|
- A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at a sp...
Text Solution
|
- A particle starts moving from rest under uniform acceleration it trave...
Text Solution
|
- At time t = 0, two bodies A and B at the same point. A moves with cons...
Text Solution
|
- A motorcyclist drives from A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h^(-1)...
Text Solution
|
- A body starts from rest and moves with constant acceleration for t s....
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration of a moving body can be found from
Text Solution
|
- A stone falls freely under gravity. It covered distances h1, h2 and h3...
Text Solution
|