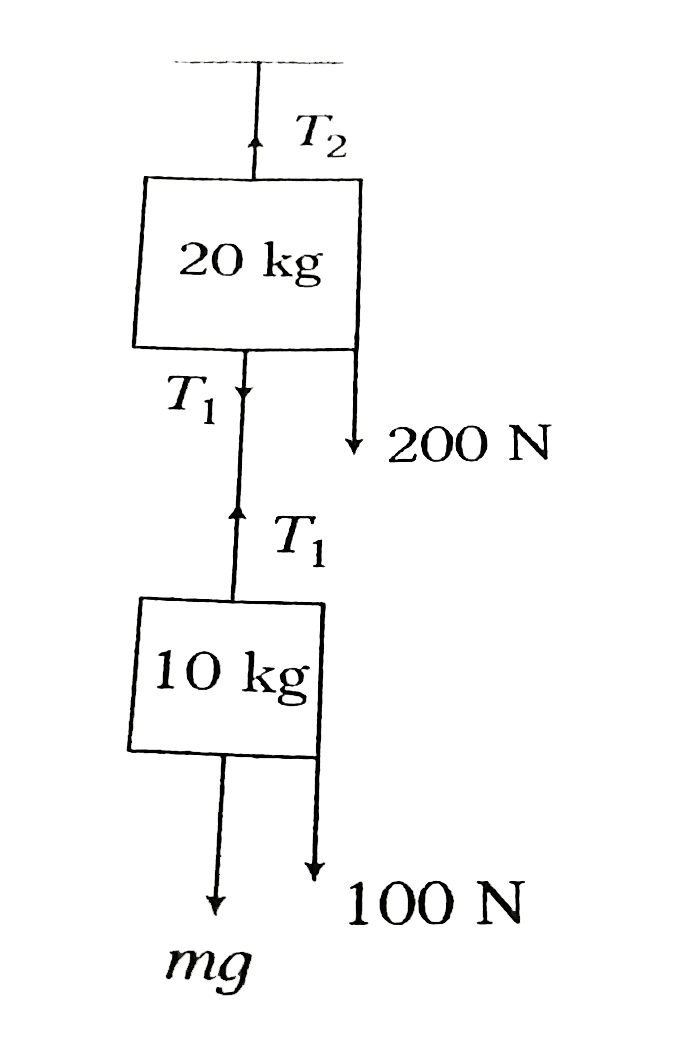Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELASTICITY-Example
- If the angle of shear is 30^(@) for a cubical body and the change in l...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 2 kg and 3kg are connected by a metal wire going ...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires shown in figure are made of the same material which has a br...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a solid cube which is subjected to a pressure of 6xx10^(5) Nm...
Text Solution
|
- If a wire of length 4 m and cross-sectional area of 2 m^(2) is stretch...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of length 4 m and diameter 5 mm is strethed by 5 kg-wt. F...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the elongation of the steel bar 1m long and 1.5 cm^(2) cross...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is replaced by another wire of same length and material but of ...
Text Solution
|
- A bar of mass m and length l is hanging from point A as shown in figur...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AD consisting of three segments AB,BC and CD joined together is ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of weight 10 N is fastened to one end of wire of cross-section...
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg mass is suspended by a rubber cord 2 m long and of cross-sectio...
Text Solution
|
- A light rod of length of length 2 m is suspended from a ceiling horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod of cross-sectional area 16 cm^(2) and two brass rods each ...
Text Solution
|
- How much should the pressure on a litre of water be changed to compres...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the decrease in volume of 100 cm^(3) of water under press...
Text Solution
|
- Find the decrease in the volume of a simple of water from the followin...
Text Solution
|
- What is the density of lead under a pressure of 2xx10^(8)Nm^(-2) , if ...
Text Solution
|
- The bulk modulus of water is 2.3 xx 10^(9) Nm^(-2). (i) Find its com...
Text Solution
|
- A 4 cm cube has its upper face displaced by 0.1 mm by a tangential for...
Text Solution
|