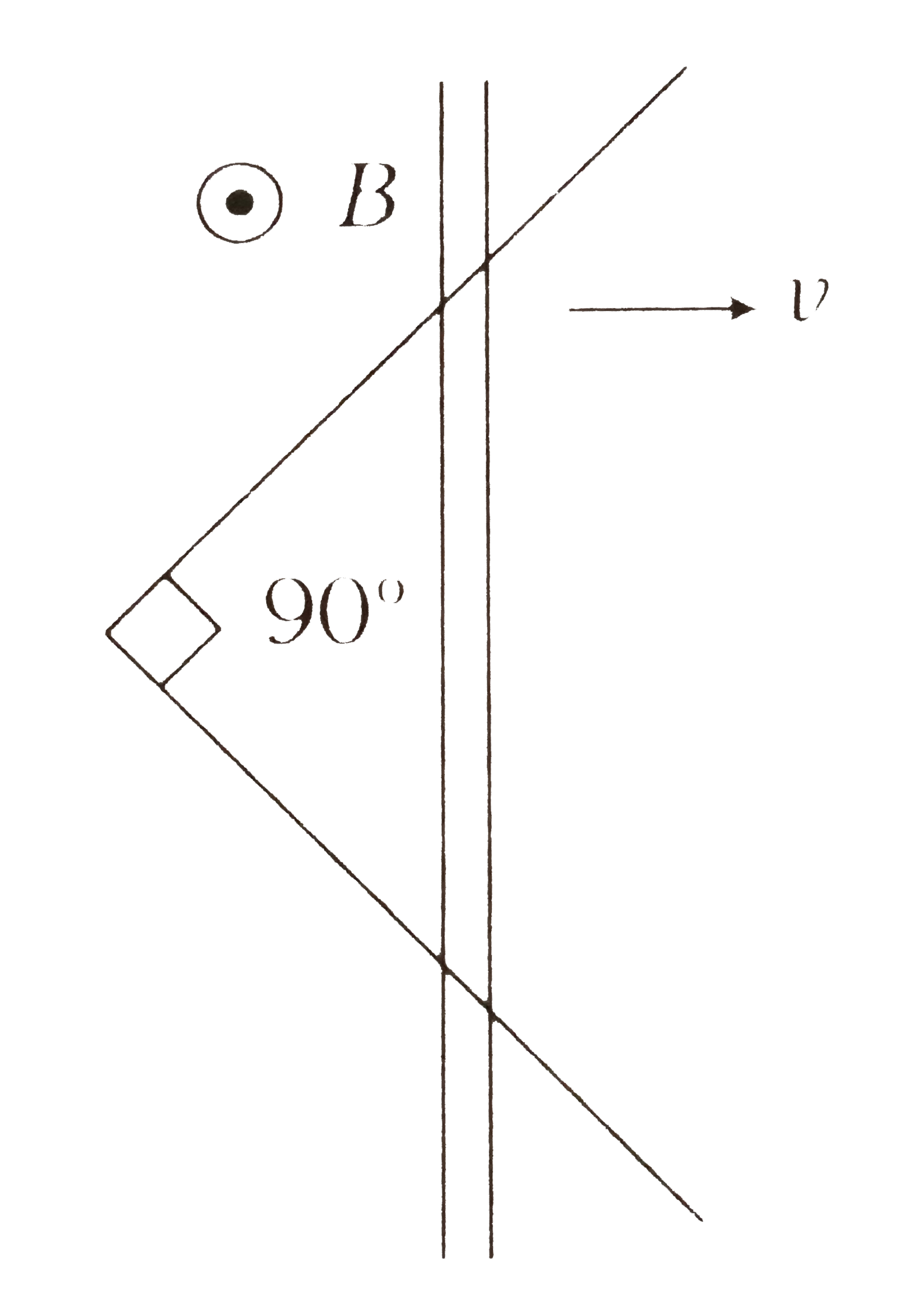
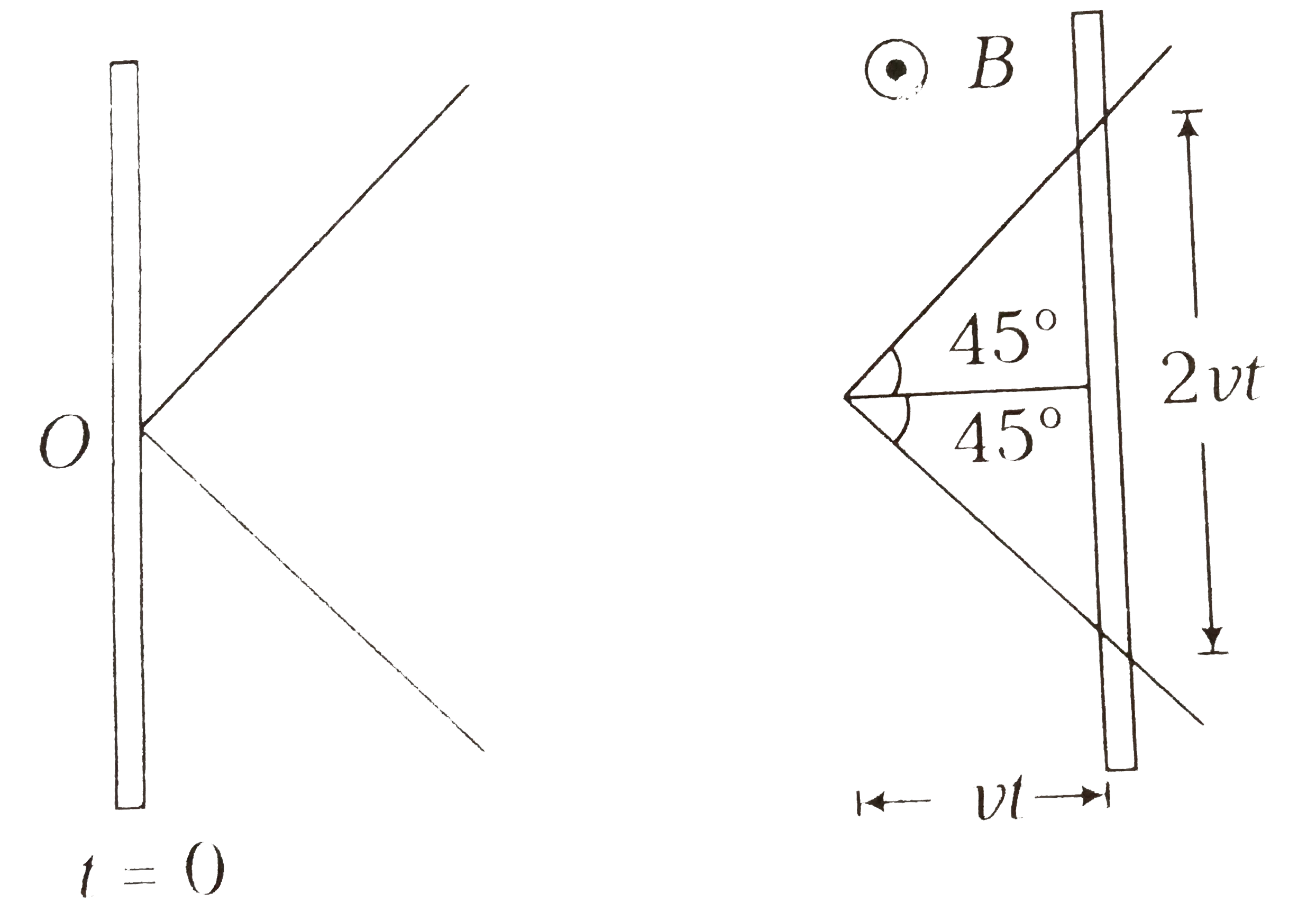
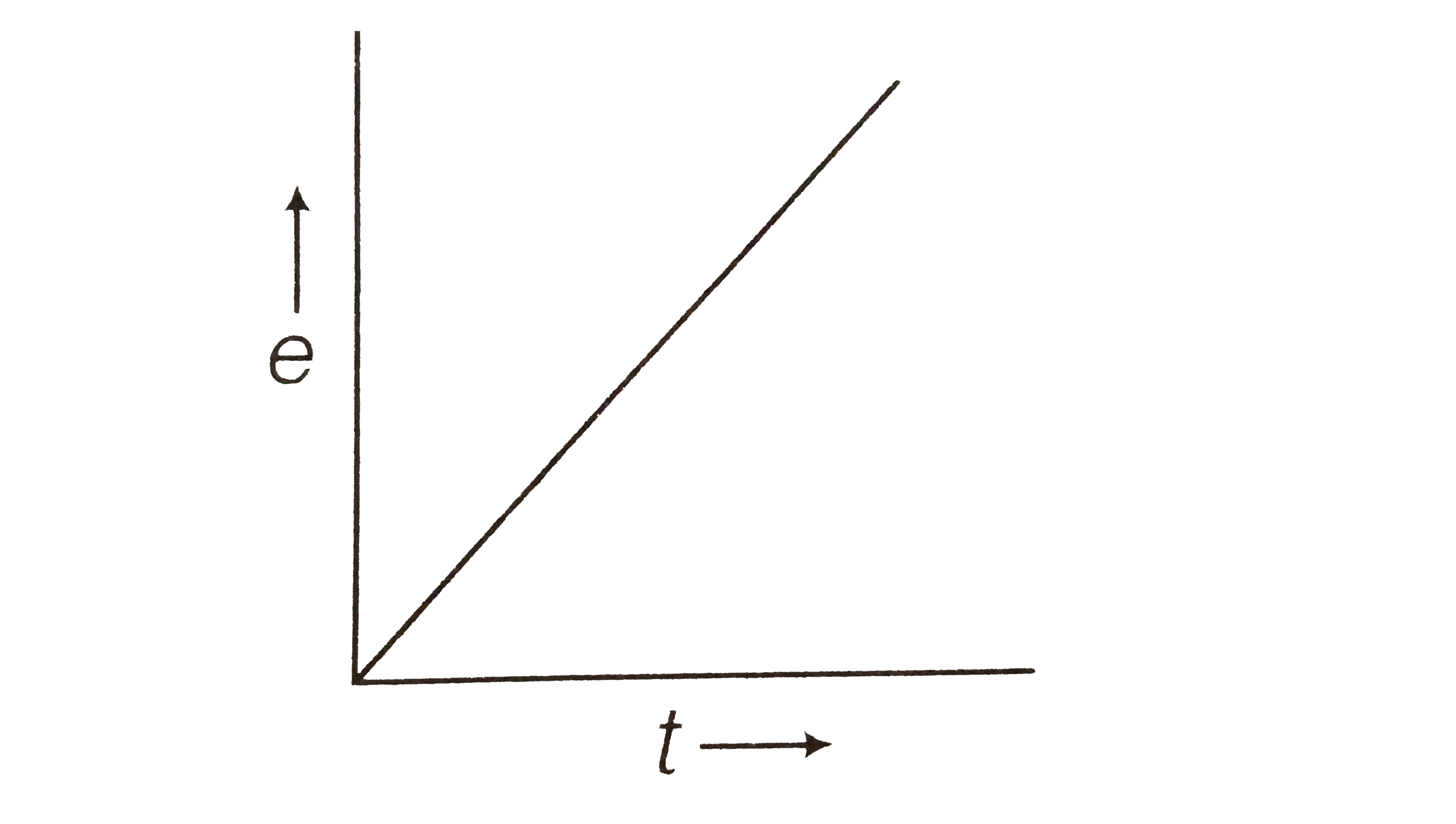
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Medical entrances gallery
- The two conducting rails are placed perpendicular to each other, such ...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid has 1000 turns. When a current of 4A flows through it,...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field is restricted within a region of radius r. Th...
Text Solution
|
- The self-inductane of a coil having 500 turns is 50 mH. The magnetic f...
Text Solution
|
- The phase difference between the flux linkage and the induced e.m.f. i...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular copper coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field of ind...
Text Solution
|
- Changing magnetic fields can set up current loops in nearby metal bodi...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of 10 cm length is moving perpendicular to uniform magnetic fiel...
Text Solution
|
- The identical loops of copper and aluminium are moving with the same s...
Text Solution
|
- A straight conductor 0.1 m long moves in a uniform magnetic field 0.1 ...
Text Solution
|
- The initial rate of increase of current, when a battery of emf 6 V is ...
Text Solution
|
- The current flows from A to B as shown in the figure. What is the dire...
Text Solution
|
- A very small circular loop of radius a is initially (at t = 0) coplana...
Text Solution
|
- A straight conductor of length 0.4 m is moved with a speed of 7 m/s pe...
Text Solution
|
- The current in self -inductance L=40 mH is to be be increased uniform...
Text Solution
|
- The induced emf in a coil of 10 H inductance in which current varies f...
Text Solution
|
- A conductor of length 5 cm is moved paralllel to itself with a speed o...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical coils A and B are kept on a horizontal tube side by side...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular coil of 100 turns and size 0.1mxx0.05m is placed perpend...
Text Solution
|
- Electromagnetic induction is not used in
Text Solution
|
- Two coils have the mutual inductance of 0.05 H. The current changes in...
Text Solution
|