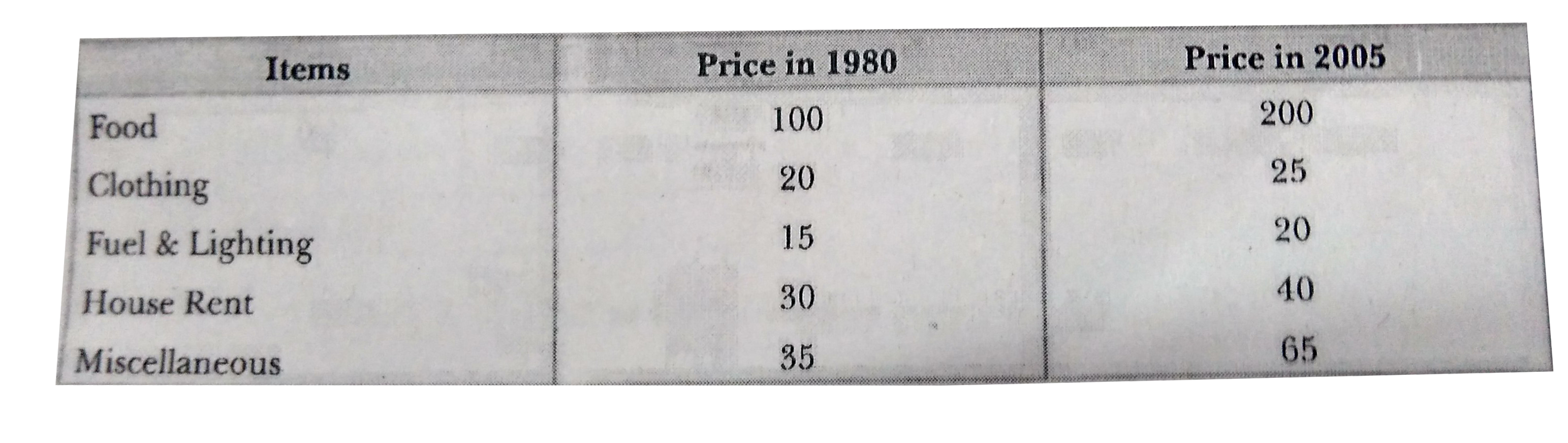Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
TARUN JAIN & VK OHRI-INDEX NUMBERS-NCERT Questions (With Hints to Answers)
- An index number which accounts for the relative importance of the item...
Text Solution
|
- In most of the weighted index numbers the weight pertains to: (i) b...
Text Solution
|
- The impact of change in the price of a commodity with little weight in...
Text Solution
|
- A consumer price index measures changes in: (i) retail prices (ii)...
Text Solution
|
- The item having the highest weight in consumer price index for industr...
Text Solution
|
- In general, inflation is calculated by using: (i) wholesale price i...
Text Solution
|
- Why do we need an index number ?
Text Solution
|
- What are the desirable properties of the base period ?
Text Solution
|
- What does a consumer price index for industrial workers measure ?
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between a price index and a quantity index ?
Text Solution
|
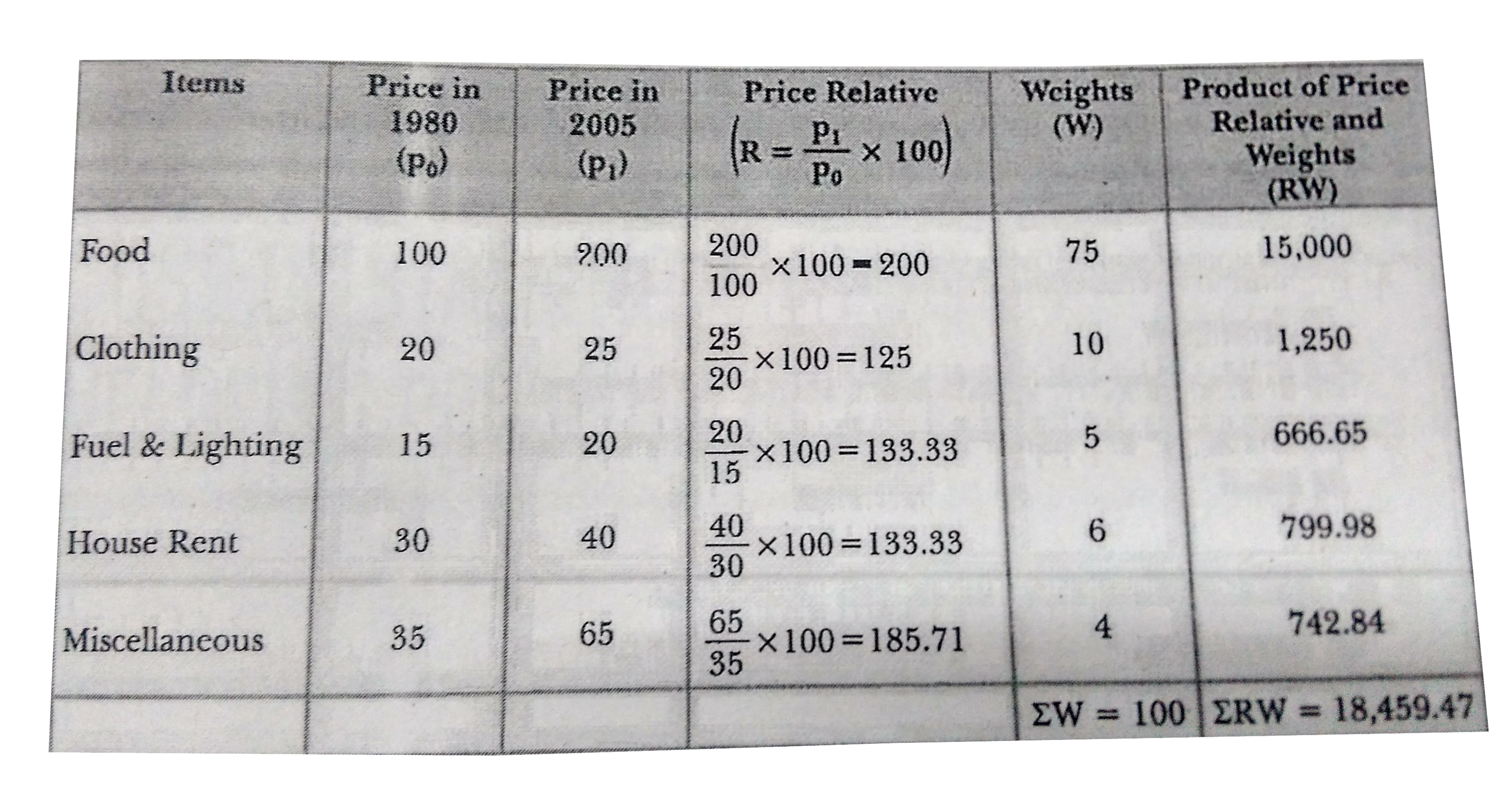
- The monthly per capita expenditure incurred by workers for an industri...
Text Solution
|
- An enquiry into the budgets of the middle class families in a certain ...
Text Solution
|