Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN-TRIANGLES-Revision Exercise (long Answer Type Question)
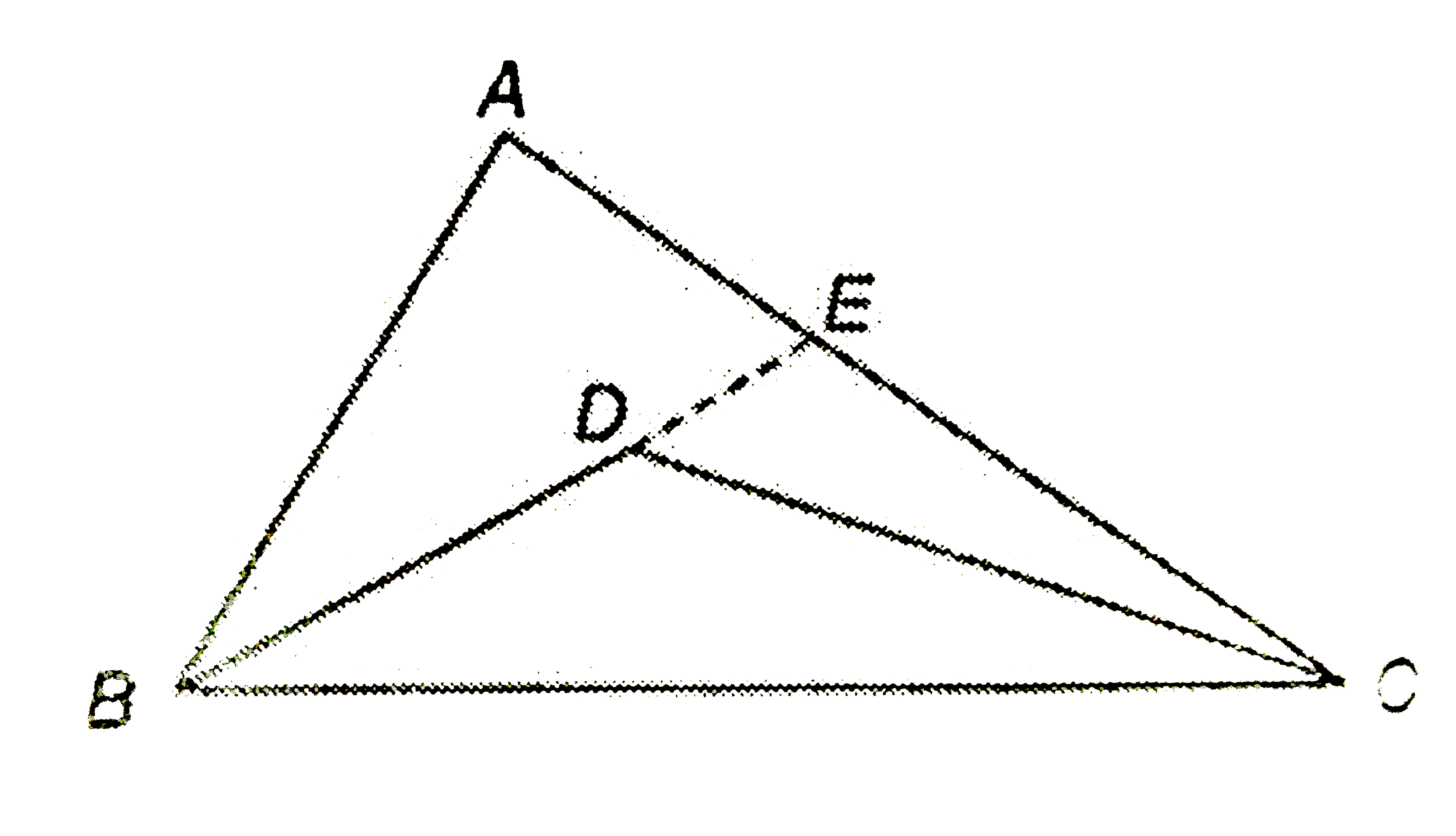
- In the adjoining figure, ABC is a triangle and D is any point in its i...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, if x = y and AB = CB, then prove that AE = CD.
Text Solution
|
- ABC is a triangle, right angled at B. If BCDE is a square on side BC a...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, ABC is an equilibrium triangle, PQ||AC and AC is ...
Text Solution
|
- The given figure shows a quadrilateral ABCD. Prove that : AB+BC+CD+D...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, the diagonals AC and BD of a quadrilateral AB...
Text Solution
|
- Let O be any point in the interior of DeltaABC, prove that : AB+BC+C...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure BO and CO are the bisectors of angleCBD and an...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure, if AD = DE. Prove that : AB+BC gt CE
Text Solution
|