Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN-AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLES-Revision Exercise (long Answer Question)
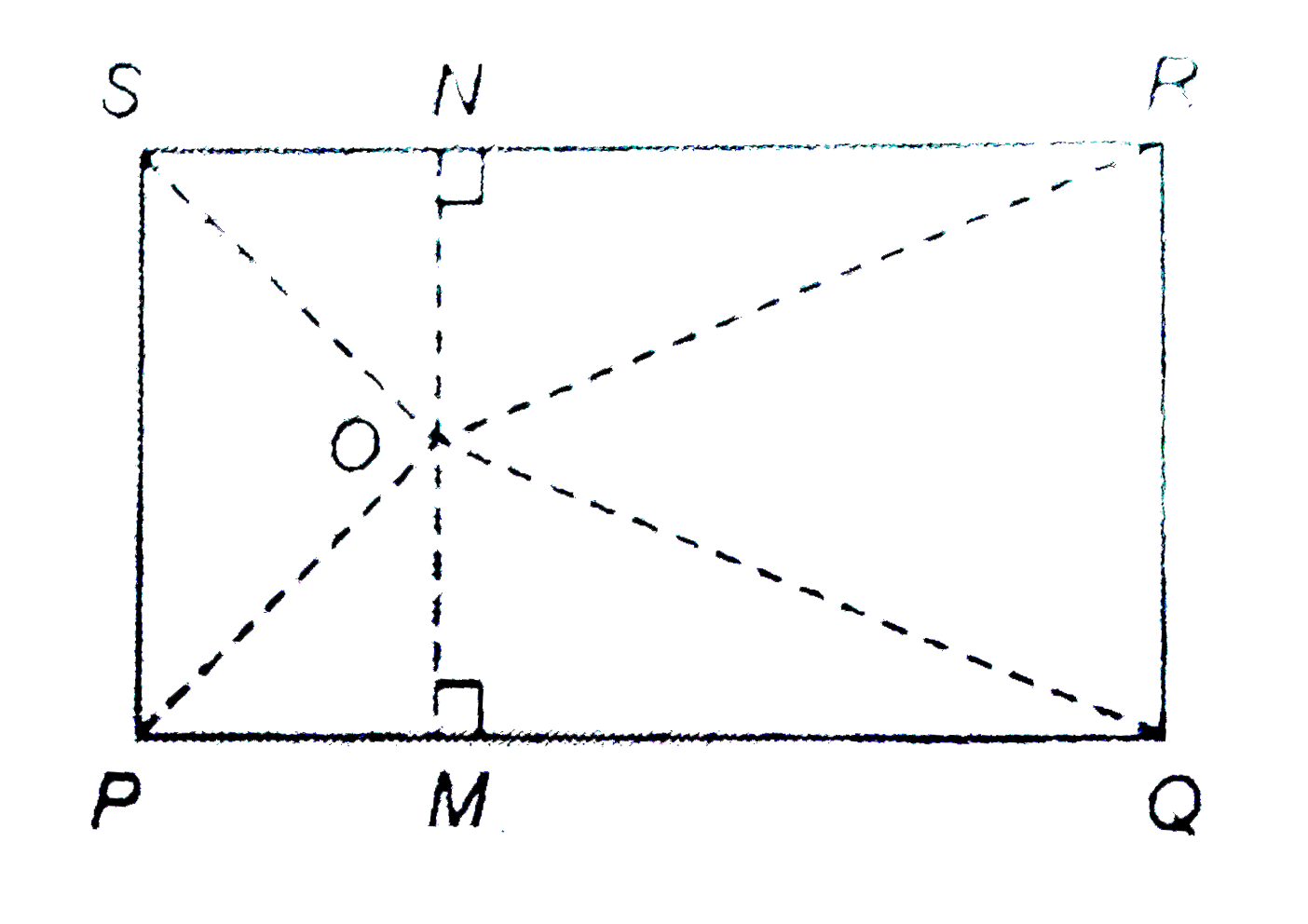
- The vertices of a rectangle PQRS are joined from an interior point 'O'...
Text Solution
|
- In Delta ABC, D is the mid-point of AB and P is any point on BC. If CQ...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, CD || AE and CY || BA. Prove that ar (DeltaCBX) = ar (Delta...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, AP ||BQ ||CR. Prove that ar(Delta AQC) = ar (Delt...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, BC||XY, BX||CA and AB ||YC. Prove that area (Delt...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the diagonals of a parallelogram divide it into four tria...
Text Solution
|