Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICALS WITH SOLUTIONS|22 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise TWO MARKS QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS|59 VideosQUESTION PAPER 2019
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise PART - C|6 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise OPTIONAL NUMERICALS WITH SOLUTIONS|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUBHASH PUBLICATION-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-FIVE MARKS QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
- S.T f=(R )/(2) in the case of a spherical mirror where symbols have ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a ray diagram to obtain the virtual image formation in (i) a conc...
Text Solution
|
- Derive mirror equation.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the phenomenon of total internal reflection.
Text Solution
|
- Write a short note on optical fibres.
Text Solution
|
- Derive referaction formula (for object in air and image in the denser...
Text Solution
|
- Derive th lens maker's formula.
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for effective focal length of two thin lenses ke...
Text Solution
|
- Express the combined power of two lenses, one of focal length +f(1) a...
Text Solution
|
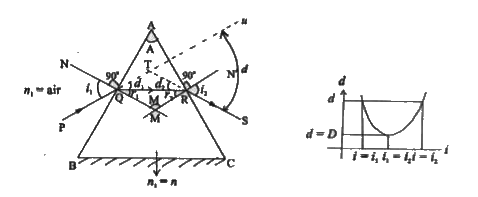
- Show that n=(sin((A+D)/(2)))/(sin((A)/(2))) where symbols have their ...
Text Solution
|