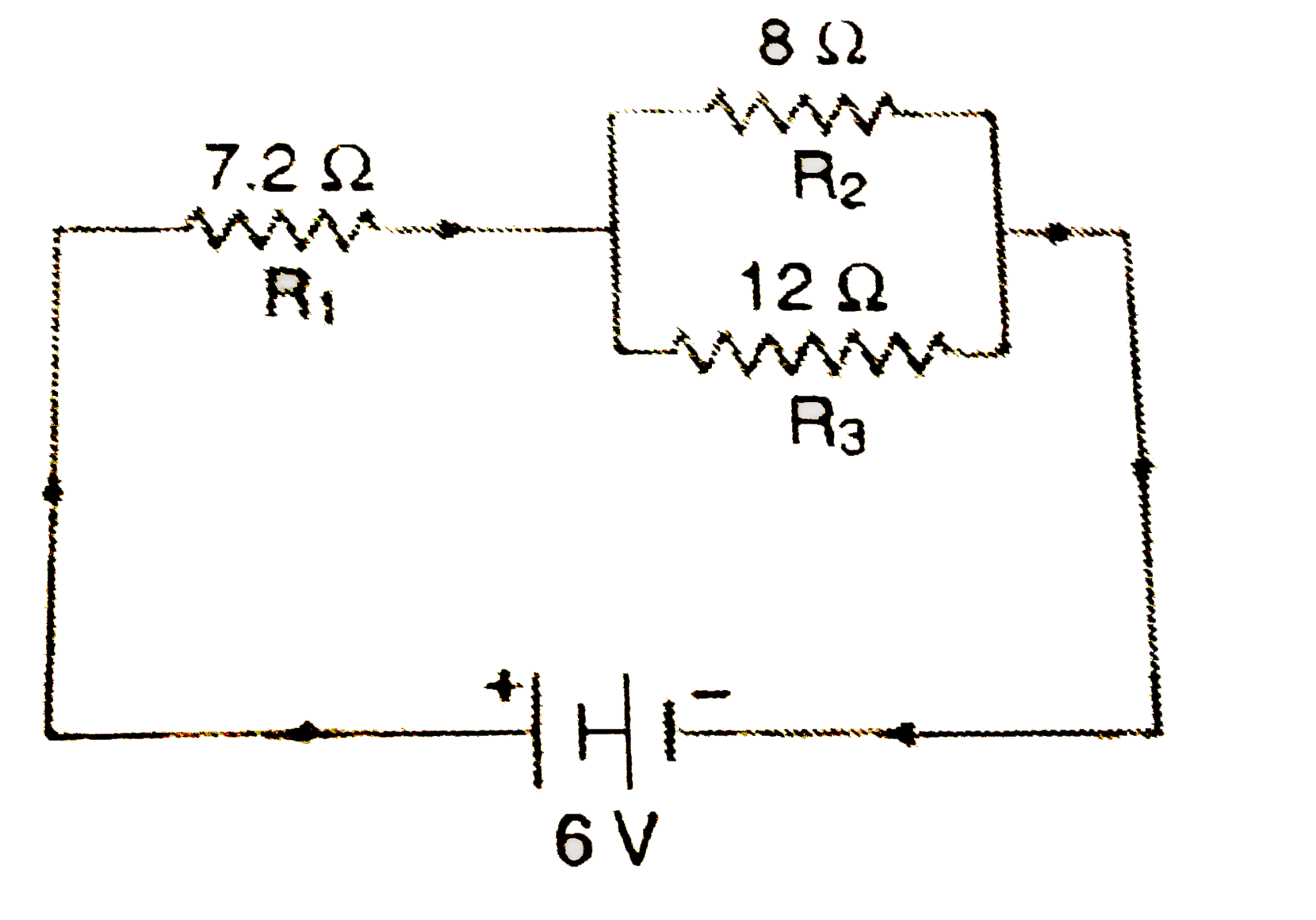
In this problem the resistances are connected in series as well as in parallel combination. For example, the two resistances `R_(2)` and `R_(3)` are in parallel combination to each other but, taken together, they are in series combination with the resistance `R_(1)`.
(i) Calculation of Total Resistance. We will now find out the total resistance of the circuit. For doing this, let us first calculate the resultant resistance R of `R_(2)` and `R_(3)` which are connected in parallel.
Now, `(1)/(R) = (1)/(R_(2))+(1)/(R_(3))`
Here, `R_(2) = 8 Omega`
and, `R_(3) = 12 Omega`
So, `(1)/(R) = (1)/(8)+(1)/(12)`
or `(1)/(R) = (3+2)/(24)`
`(1)/(R) = (24)/(5)`
and `R = 4.8` ohms
Thus. the two resistance of 8 ohms and 12 ohms connected in parallel are equal to a single resistance of 4.8 ohms. It is obvious that in the abive given diagram, we can replace the two resistance `R_(2)` and `R_(3)` by a single resistance of 4.8 ohms. We can draw another circuit diagram for this problem by showing a single resistance of 4.8 ohms in place of two parallel resistances. Such a circuit diagram is given alonside.
It is clear from this diagram that now we have two resistances of 7.2 ohms and 4.8 ohms which are connected in series. So,
Total resistance `= 7.2 +4.8`
= 12 ohms

Thus, the total resistance of the circuit is 12 ohms.
(ii) Calculation of Total Current. The battery shown in the given circuit is of 6 volys. So
Total potential difference, `V = 6` volts
Total current, `I = ?` (To be calculated)
and Total resistance, `R = 12` ohms (Calculated above)
So, applying Ohm's law to the whole circuit, we get:
`(V)/(I) = R`
or `(6)/(I) = 12`
or `12I = 6`
or `I = (6)/(12)`
`I = (1)/(2)`
So, Total current, `I = 0.5` ampere (or 0.5A)
Thus, the total current flowing in the circuit is 0.5 ampere. It should be noted that the same current flows through all the parts of a series circuit. So, the current flowing through the resistance `R_(1)` is also 0.5 ampere.
(iii) Calculation of Potential Difference Across `R_(1)`. We have now to find out the potential difference across the resistance `R_(1)` of 7.2 ohms.
Now, Potential difference across `R_(1) = ?` (To be calculated)
Current through `R_(1) = 0.5` ampere
And, Resistance of `R_(1) = 7.2` ohms
Applying Ohm's law to the resistance `R_(1)` only, we get:
`(V)/(I) = R`
or `(V)/(0.5) = 7.2`
or `V = 7.2 xx 0.5`
opr `V = 2.6` volts
Thus, the potential difference across the ends of the resistances `R_(1)` is 3.6 volts.