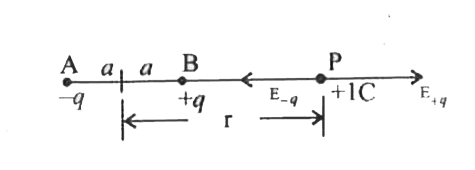
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUBHASH PUBLICATION-SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER JULY 2017-QUESTION
- Write Maxwell's equation for the speed of electromagnetic waves and ex...
Text Solution
|
- What are de-Brogli Waves ? How does the de-Broglie wavelength vary wit...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the block diagram of generalised communication system.
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the relation between electric field and electric potential due ...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the relation vec(j)=sigmavec(E) with terms which has usual mean...
Text Solution
|
- How can a moving coil galvanometer be converted into a voltmeter? Expl...
Text Solution
|
- Mention any three application of eddy currents.
Text Solution
|
- Define critical angle. Write two conditions for total internal reflect...
Text Solution
|
- Write any three difference between interference and diffraction.
Text Solution
|
- Define the terms : Threshold frequency
Text Solution
|
- Define the terms : Work function.
Text Solution
|
- Define the terms : Stopping potential.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the use Zener diode as a voltage regulator.
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for electric field due to an electric dipole at a...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for the force between two straight parallel condu...
Text Solution
|
- Show that a current carrying solenoid is equivalent to a bar magnet.
Text Solution
|
- Derive th lens maker's formula.
Text Solution
|
- Derive an experession for the total energy of an electron in stationar...
Text Solution
|
- What is amplification? With a circuit diagram, explain the working of ...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each has an...
Text Solution
|