Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUBHASH PUBLICATION-SUPPLEMENTARY EXAM QUESTION PAPER JUNE 2018-QUESTION
- Write any three properties of magnetic field lines.
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for effective Capacitance of two Capacitors Conne...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substances.
Text Solution
|
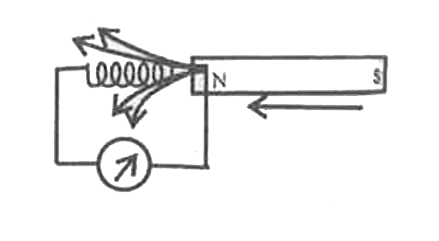
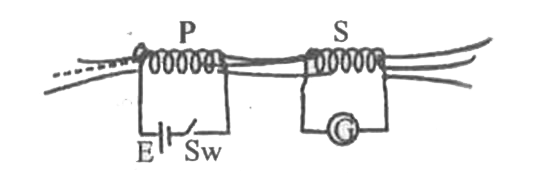
- Describe the coil and barmagnet experiment to demonstrate the phenomen...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for effective focal length of two thin lenses ke...
Text Solution
|
- Write any three experimental observations of photoelectric effect
Text Solution
|
- Explain the working of a zener diode as a voltage regulator.
Text Solution
|
- What is the function of 'receiver' in communication system ? Draw the ...
Text Solution
|
- Using Gauss's law in electrostatics, obtain an expression for electric...
Text Solution
|
- Derive sigma = (n e^(2) tau)/(m) where the symbols have their usual ...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for the force between two straight parallel condu...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the expression for fringe width in the case of interference of ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe with suitable block diagrams, action of pn-junction dioid...
Text Solution
|
- Assuming the expression for radius of the orbit, derive an expression ...
Text Solution
|
- The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 100 cm^(2) e...
Text Solution
|
- The plates of a parallel plate capacitor have an area of 100 cm^2 ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit diagram , calculate : The main current thr...
Text Solution
|
- A 20 Omega resistor, 1.5 H inductor and 35 mu H capacitor are connecte...
Text Solution
|
- The radii of curvatore of two surfaces of a convex lens is 0.2 m and 0...
Text Solution
|
- The half life of ""(38) Sr^(90) isotope is 28 years. What is the rate ...
Text Solution
|