Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
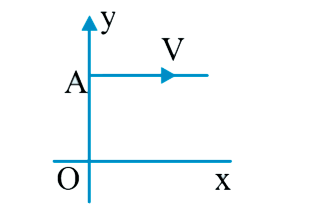
- A body of mass m is moving with a constant velocity along a line paral...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle performs uniform circular velocity along a line parallel to...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to t...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving in the xy-plane with a constant velocity along a ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is moving with a constant velocity along a line paral...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is moving with a constant velocity along a line paral...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving with a contant velocity along a line parallel to ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving with a contant velocity along a line parallel to ...
Text Solution
|