Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
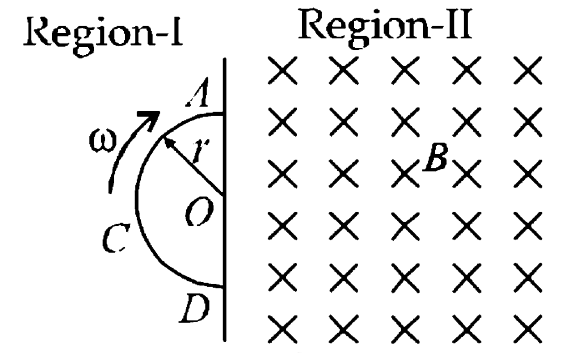
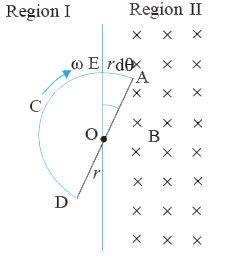
- Space is divided by the line AD into two regions. Region I is field fr...
Text Solution
|
- A wire loop confined in a plane is rotated in its oen plane with some ...
Text Solution
|
- Space is divided by the line AD into two regions. Region I is field fr...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop of wire carrying current I is lying in the plane of pape...
Text Solution
|
- There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the ...
Text Solution
|
- A space is divided by the line AD into two regions. Region I is field ...
Text Solution
|
- A space is divided by the line AD into two regions. Region I is field ...
Text Solution
|
- A space is divided by the line AD into two regions. Region I is field ...
Text Solution
|
- There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the ...
Text Solution
|