Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINEMATICS
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise Textbook questions & answers (IV. Numerical problems).|48 VideosKINEMATICS
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise Other important questions & answers (I.Multiple choice questions).|236 VideosKINEMATICS
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise Textbook questions & answers (II. Short answer questions).|30 VideosGRAVITATION
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTION & ANSWERS (CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS)|34 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (VI. Conceptual Questions.)|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS-KINEMATICS -Textbook questions & answers (III. Long answer questions).
- If \vec { A } = 8 \hat { i } + 6 \hat { j } and \vec { B } = 4 \hat { ...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the properties of scaiar and vector
Text Solution
|
- Derive the kinematic equations of motion for constant acceleration .
Text Solution
|
- Derive the equations of motion for a particle Falling vertically
Text Solution
|
- Derive the equations of motion for a particle (a) falling vertically (...
Text Solution
|
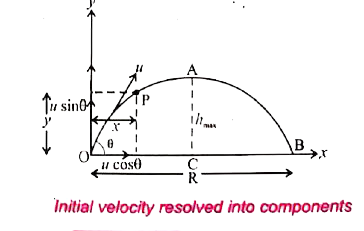
- Derive the equation of motion, range and maximum height reached by th...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for centripetal acceleration.
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for total acceleration in the non-uniform circul...
Text Solution
|
- Explain in detail the triangle law of addition.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the properties of scalar and vector
Text Solution
|
- Derive the kinematic equations of motion for constant acceleration.
Text Solution
|
- Derive the equations of motion for a particle (a) falling vertically (...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the equations of motion for a particle (a) falling vertically (...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum height attained by a projectile when thrown at an angle th...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for centripetal acceleration.
Text Solution
|
- Derive the expression for total acceleration in the non-uniform circul...
Text Solution
|